Osteoblasts are the major cellular component of bone usually involved in the initial formation and mineralization of bones. The osteoblast the bone cell responsible for forming new bone is found in the growing portions of bone including the periosteum and endosteum.

Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts are the two types of bone cells which constitute the bone tissue or the osseous tissue.
Where are the osteogenic layers of osteoblast and osteoclast found. Where are the osteogenic layers of osteoblast and osteoclast found. Types of Bone Cells. Osteogenic cells are undifferentiated cells with high mitotic activity.
The existence of these self-renewing. Osteoblast Cell Osteoprogenitor cells Osteoclast cells and Osteocytes cells Where are osteogenic cells located. Osteogenic cells or Osteoblasts are found in the bone.
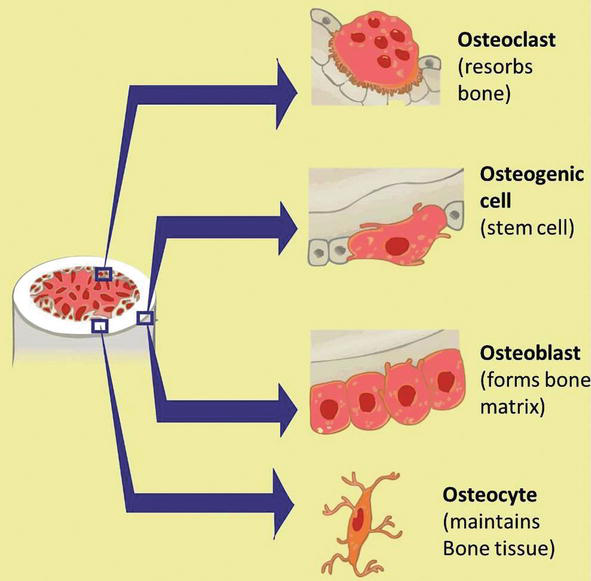
Osteoblasts are found in large numbers in the periosteum the thin connective tissue layer on the outside surface of bones and in the endosteum. Normally almost all of the bone matrix in the air breathing vertebrates is mineralized by the osteoblasts. Bone consists of four types of cells.
Osteoblasts osteoclasts osteocytes and osteoprogenitor or osteogenic cells. Each cell type has a unique function and is found in different locations in bones. The osteoblast the bone cell responsible for forming new bone is found in the growing portions of bone including the periosteum and endosteum.
The main difference between osteoblast and osteoclast is that osteoblast is involved in the formation and mineralization of bones whereas osteoclast is involved in the breakdown and resorption of bones. The osteogenic cells in bones are developed into osteoblasts. The osteoblasts secrete the collagen matrix and the calcium salts of a bone.
Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts are the two types of bone cells which constitute the bone tissue or the osseous tissue. The bone is a metabolically active tissue consisting of several types of cells among which the Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts are the most important ones. These features led the discoverers to study osteoclast extensively under light and electron microscope.
Osteoclasts showed completely different behavior as compared to other types of bone cells. The occurrence of osteoclasts is quite scarce in the bony tissue. It is estimated that in an area of 1mm of the bony tissue almost 2 to 3 osteoclasts are found.
Osteoblast-Osteoclast activity 1. Dr Gauri Kapila MDS Student Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology 2. Portion of maxilla and mandible that forms supports protects the teeth Parts alveolar bone proper compact bone cancellous bone FUNCTIONS Support to teeth Attachment to muscles Framework for bone marrow Reservoir of ions.
Osteoblasts are usually found on the surface of new bone arranged in a monolayer. There are a lot of hairy short protrusions on the surface of osteoblasts that are connected to adjacent cells and penetrate the surrounding bone-like tissue forming a network structure. Start studying Osteoblasts Osteoclasts Osteogenic Cells Osteocytes Compact Bone Spongy Bone.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Our results demonstrate that there are two types of layers in osteogenic differentiation that have not been explored previously.
The upper layers which are collagenase I sensitive. And the lowest layer attached to the substrate which is trypsin sensitive only. It must be noted that in our experiments the use of trypsin only until day 15 showed an effect on all of the layers and detached all of the cells.
Outer fibrous layer is dense irregular connective tissue The collagen fibers from the outer layer connect the the collagen fiber sin the inner layer Inner osteogenic layer. The osteoblast-like cells express osteogenic transcription factors and genes such as runt-related transcription factor 2 Runx2 osterix Msh homeobox Msx SRY-box transcription factor 9 SOX9 and alkaline phosphatase ALP bone sialoprotein BSP and osteocalcin OC all of which play a central role in bone mineralization. Immature osteogenic cells are found in the deep layers of the periosteum and the marrow.
When they differentiate they develop into osteoblasts. The dynamic nature of bone means that new tissue is constantly formed while old injured or unnecessary bone is dissolved for repair or for calcium release. Also Know are osteogenic cells stem cells.
Osteoprogenitor cells are derived. He grants that young cartilage cells or chondroblasts or young bone cells or osteoblasts have attained certain specificity but the lining cell of bone which has been termed the osteogenic cell demonstrates capability to proceed along either the cartilage or bone pathway. Ars that environmental conditions in the areas of membrane bone formation are suitable for the differentiation of osteogenic cells into bone.
Osteoblasts are the major cellular component of bone usually involved in the initial formation and mineralization of bones. The osteoblasts the bone cell responsible for forming new bone it is found in the growing portions of bone including the periosteum and endosteum.