
We propose that E33 IgG binding on mature virions orients the Fc region in a manner that impacts subsequent antibody binding to nearby sites. Why antibodies are fragmented.
In particular modifications in antibodys Fc fragment crystallizable region can provide multiple benefits such as added toxicity by drug conjugation higher affinity to Fc receptors on immunocytes or the addition of functional modules.
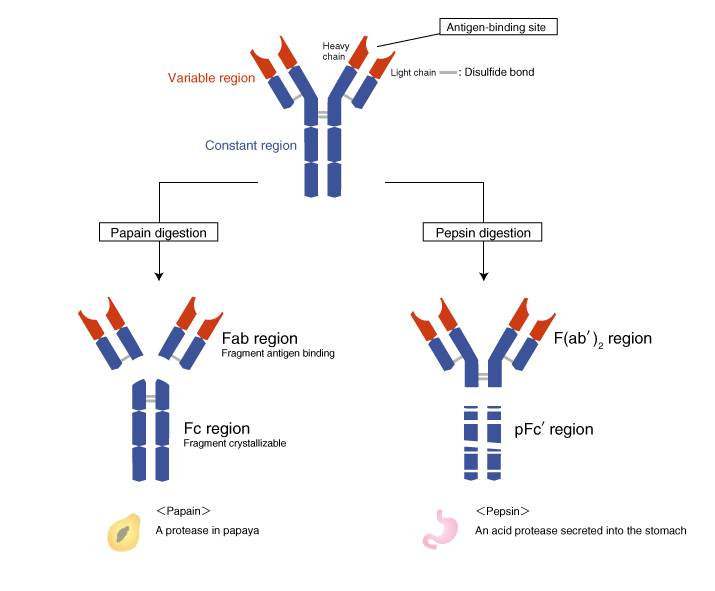
What is fc region of antibody. The hinge region that links the Fc and Fab portions of the antibody molecule is in reality a flexible tether allowing independent movement of the two Fab arms rather than a rigid hinge. This has been demonstrated by electron microscopy of antibodies bound to haptens. The Fc portion as well as one domain of both the heavy and light chain of the Fab region has a constant amino acid sequence and is referred to as the constant region C region of the antibody and defines the class and subclass of each antibody.
The Fc portion is responsible for the biological activity of the antibody Figures 1-3 however the Fc portion only becomes biologically. Fc region is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This property allows antibodies to activate the immune system.
The Fc regions of immunoglobulin Gs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Immunoglobulins and Fc receptors are critical glycoprotein components of the immune system. Fc receptors bind the Fc effector region of antibody molecules and communicate information within the innate and adaptive immune systems.
Glycosylation of antibodies particularly in the Fc region of IgG has been extensively studied in health and disease. In particular modifications in antibodys Fc fragment crystallizable region can provide multiple benefits such as added toxicity by drug conjugation higher affinity to Fc receptors on immunocytes or the addition of functional modules. However the generation of recombinant antibodies requires multiple laborious bioengineering steps.
The antigen-binding regions can be derived by proteolytic cleavage of the antibody to generate antigen-binding fragments Fab and the constant fragment Fc also known as the fragment of crystallization. The Fab comprises the variable regions variable heavy VH 11 and variable light VL and constant regions C H1 and CkCl. The universal structure of antibody includes the constant regions part of the fragment crystallizableFc region of the antibody shown in dark blue.
It also includes the fragment antigen binding which is composed of one heavy and one light chain shown as L for light and H for heavy. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity ADCC is mediated through the engagement of the Fc segment of antibodies with Fcγ receptors FcγRs on immune cells upon binding of tumor or viral antigen. We have engineered the Fc region of a human immunoglobulin G IgG to generate a mutated antibody that modulates the concentrations of endogenous IgGs in vivo.
This has been achieved by targeting the activity of the Fc receptor FcRn which serves through its IgG salvage function to maintain and regulate IgG concentrations in the body. Fc receptor is a antibody receptor involved in antigen recognition which is located at the membrane of certain immune cells including B lymphocytes natural killer cells macrophages neutrophils and mast cells. Such receptors recognize Fc fragment of antibodies and that is the name of Fc receptor derived from.
In cancer immunotherapy some IgG1 antibodies rely on the Fc-mediated immune effector function antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity ADCC as the major mode of action to deplete tumor cells. It is well-known that this effector function is modulated by the N. Structural requirements in the Fc region of rabbit IgG antibodies necessary to induce cytotoxicity by human lymphocytes.
Michaelsen TE Wisloff F Natvig JB. Rabbit IgG anti-chicken erythrocyte antibodies were compared with the Fabc or Facb fragments of IgG and with partially reduced and alkylated IgG for the capacity to induce cytotoxicity by normal human lymphocytes. We propose that E33 IgG binding on mature virions orients the Fc region in a manner that impacts subsequent antibody binding to nearby sites.
This Fc-mediated steric constraint is a novel mechanism by which the maturation state of a virion modulates the efficacy of the humoral immune response to flavivirus infection. 24109224 Indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. Research Support NIH Intramural.
Fab antibody fragments are used in assay systems where the presence of the Fc region may cause problems. In these cases it is preferable to use only the antigen binding Fab portion of an antibody. Why antibodies are fragmented.
Proteolytic cleavage of antibodies results in defined antibody. From a study of the effect of various antigenantibody ratios it is concluded that the 28-unit-saccharide-induced changes in the GdIII environment in the Fc region are caused by the specific geometrical structure of the antigen-antibody complexes formed and not simply by occupancy of the combining sites on the antibody. The Fc-region of a new class of intact bispecific antibody mediates activation of accessory cells and NK cells and induces direct phagocytosis of tumour cells.
Br J Cancer 83 261266 2000.