The term thermal power is usually used because it means the rate at which heat is produced in the reactor core as the result of fissions in the fuel. The term thermal power is usually used because it means the rate at which heat is produced in the reactor core as the result of fissions in the fuel.

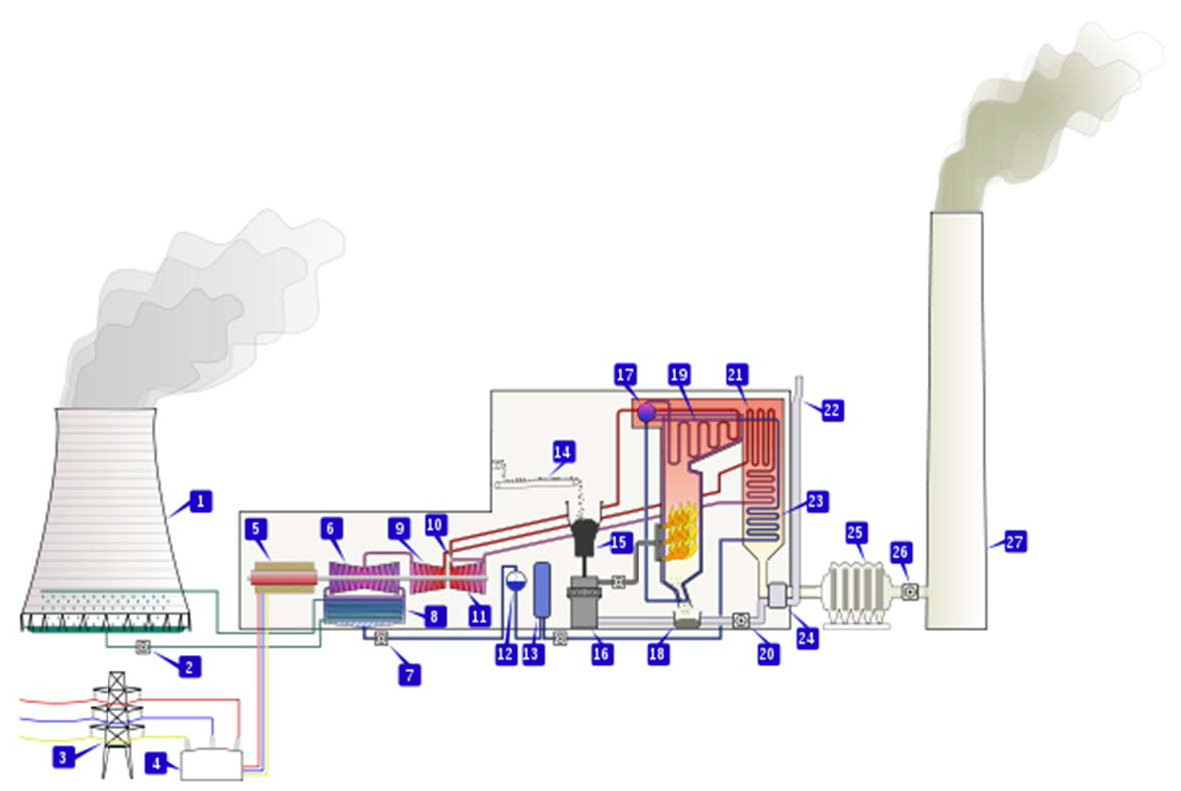
A generating station which converts heat energy of coal combustion into electrical energy called thermal power plant.
Thermal and nuclear power plant. In a nuclear plant the heat source is from the nuclear reaction whereas in a thermal power plant it is from the combustion of coal. The difference is in the inlet steam parameters to the turbine in a nuclear plant. Thermal power plants use steam at superheated conditions.
Nuclear power plant Thermal power station. Where there is enough supply of water away from thickly populated areas to avoid radioactive pollution. Power plant located at a place where ample supply of water and coal is available transportations facilities are adequate.
Required least compare to TPP HPP of same capacity. The Nuclear Power Plant consists of 7 Main Parts. Nuclear Reactor Coolant circulating pump Heat Exchanger Feed pump Condenser Turbine and Generator.
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power plant whose source of energy is nuclear energy. Its operation is similar to any other thermal power plant. Thermal energy is generated from an energy source.
Steam is generated with the thermal energy generated. A generating station which converts heat energy of coal combustion into electrical energy called thermal power plant. This power plant also referred to as a steam power plant.
This power plant basically works on a Rankine cycle. In this power plant steam is produced in the boiler by utilizing the heat of coal combustion in a chamber. In the 18 th century the Thermal Power Plant exists with a lot of improvements in the reciprocating steam engine This reciprocating steam engine is used to develop the steam and with the use of an electric generator makes or produces the electricity.
Thermal and nuclear power 1. THERMAL AND NUCLEAR POWER. Karachi Nuclear Power Plant and a heavy-waterKarachi Nuclear Power Plant and a heavy-water production facility in 1972production facility in 1972.
However in 1976 it abruptly stopped supplying fuelHowever in 1976 it abruptly stopped supplying fuel after which Pakistan started. 17 rânduri Thermal and Nuclear Power Plants Static General Knowledge is an integral. Nuclear and Thermal Power Plants Volume 12017 Nuclear Power Plants in India Name Location Narora Atomic Power Station Narora Uttar Pradesh Madras Atomic Power Station Kalpakkam Tamil Nadu Kaiga Generating Station Kaiga Karnataka Kakrapar Atomic Power Station Kakrapar Gujarat Kudankulam Atomic Power Project Kudankulam Tamil Nadu.
The term thermal power is usually used because it means the rate at which heat is produced in the reactor core as the result of fissions in the fuel. Nuclear power plants also use the total output of electrical power but this value is due to the efficiency of conversion usually from 30 to 40 always smaller than the thermal power of reactor. The basic principle of a nuclear power station is the same as a conventional thermal power station.
The only difference is that instead of using heat generated due to coal combustion here in a nuclear power plant the heat generated due to nuclear fission is. Thermal Efficiency of Nuclear Power Plants Boiler Pressure. An increase in the boiler pressure is in the result limited by material of the reactor pressure vessel.
Decreasing the turbine exhaust pressure increases the net work per cycle but also decreses the vapor. Thermal power plants are power stations which convert heat energy into electric energy. Thermal power plants the heat energy obtained from combustion of solid fuel mostly coal is used to convert water into steam this steam is at high pressure and temperature.
Nuclear energy allows to respond effectively and sustainably to growth in demand with a safe affordable low-carbon electricity. In South Africa Eskom led to a partnership for more than 30 years from the construction of the Koeberg power plant. The cooperation fields include operation and maintenance engineering and training.