
We highlight the value of applied genetics approaches for increasing aquaculture productivity and the conservation of fish genetic resources. On the whole selection is aimed at establishing food production that is increasingly ecological ethical and economical.
Plus practice selective harvesting to protect the future of fishing.
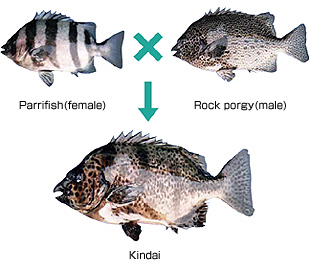
Selective breeding of fish. We illustrate that fundamental principles of genetic management are common in the implementation of both selective breeding and conservation programmes and should be emphasized in capacity development efforts. We highlight the value of applied genetics approaches for increasing aquaculture productivity and the conservation of fish genetic resources. A way to boost the production of fish in Europe Selective breeding has a very high potential for improving the genetic makeup of fish in aquaculture production.
It just takes a few generations to accomplish major improvements in economically important traits. These improvements can be achieved by using selective breeding in better and efficient breeding. Firstly an enormous potential exists to improve aquaculture productivity though the application of selective breeding programmes and capitalize on the broad genetic diversity present in many wild fish populations.
Secondly because of the lack of welldefined domesticated breeds the conservation of fish genetic resources is generally concerned with i the application of appropriate. Selective breeding is a breeding programme that tries to improve the breeding value of the population by selecting and mating only the best fish largest heaviest those with the desired colour etc in the hope that the select brood fish will be able to. Ample evidence that constraints are usually selective breeding can be financial and lack of successful in fish adequate capacity current breeding programs mostly focus on growth improvements unfavourable correlated traits must be monitoredBreeding programs in fish.
Conservationof fish genetic resources. The authors predict that within two decades selective breeding of species like barramundi will triple the internal rate of return for farms. Classical selection of superior animals may be the most effective and appropriate method to genetically improve aquacultured marine fish.
Past experience with salmon and tilapia suggest improvement rates of 10 to 20 percent per generation are possible. Advancing selective breeding will improve critical sustainability traits such as disease resistance feed efficiency and growth rates that will enhance aquaculture both from an environmental and economic perspective. Why isnt everyone already doing it.
Regular part of fish farming systems either continuously or to refresh the cultivated stocks. Furthermore selective breeding has rarely been successfully practiced in fish. The two main reasons for this has probably been the lack of controlled making and reproduction and the problems of keeping individual records of the breeding candidates.
An important part of increasing the future aquaculture production is to improve the biological productivity of farmed species of fish shellfish crustacean and molluscs and seaweeds. The role of selective breeding will therefore be discussed. Your water if you are hoping to breed them and if you hope to share the fish you breed with other hobbyists.
Find out what the basic preferred conditions are for the fish you want to breed. Minimum size tank recommended pH hardness temperature water movement amount of light need for plants places to hide whether they require gravel. Through selective breeding the angelfish have become much like goldfish in that there are now a variety of subspecies that do not exist in the wild.
Many of the subspecies of angels have multiple names but their underlying genetic makeup remains traceable through attribute and form. Anglers wanting to help will study the waterway reports. Plus practice selective harvesting to protect the future of fishing.
In many instances keeping the fish the minimum size to 3-4 inches larger is fine. There are adequate numbers of these size fish. Letting larger fish go to breed ensures more of the harvest size fish in the future.
The bettas elaborate colors and long flowing fins are the product of a millennium of careful selective breeding. Or as Yi-Kai Tea a doctoral candidate at the University of Sydney who studies. Selective breeding is when plants or animals are bred for specific traits.
These traits could be physical such as a fur color or they can be more useful such as an increase in milk production. There are many uses for selective breeding some more beneficial than others but still many people are opposed to the idea. Selective breeding of farmed fish improves the profitability of the aquaculture business and the quality of food available for consumers.
The applied selective breeding methods improve not only the production traits of fish but also their quality and health. On the whole selection is aimed at establishing food production that is increasingly ecological ethical and economical.