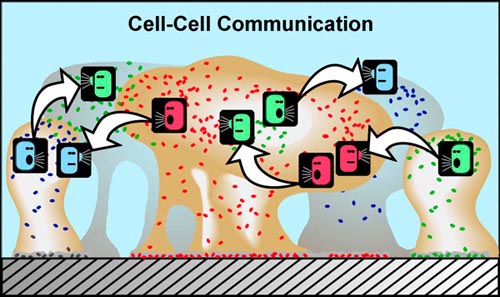
Quorum sensing is a mechanism of cell to cell signaling or density sensing in micro-organisms. Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria.

This process termed quorum sensing allows bacteria to monitor the environment for other bacteria and to alter behavior on a population-wide scale in response to changes in the number andor species present in a community.
Quorum sensing cell to cell communication in bacteria. As in higher organisms the information supplied by these molecules is critical for synchronizing the activities of large groups of cells. In bacteria chemical communication involves producing releasing detecting and responding to small hormone-like molecules termed autoinducers. This process termed quorum sensing allows bacteria to monitor the environment for other bacteria and to alter.
In bacteria chemical communication involves producing releasing detecting and responding to small hormone-like molecules termed autoinducers. This process termed quorum sensing allows bacteria to monitor the environment for other bacteria and to alter behavior on a population-wide scale in response to changes in the number andor species present in a community. Most quorum-sensing-controlled processes are unproductive when undertaken by an individual bacterium.
In bacteria chemical communication involves producing releasing detecting and responding to small hormone-like molecules termed autoinducers. This process termed quorum sensing allows bacteria to monitor the environment for other bacteria and to alter behavior on a population-wide scale in response to changes in the number andor species present in a community. Most quorum-sensing-controlled processes are unproductive when undertaken by an individual bacterium.
Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Bacteria communicate with one another using chemical signal molecules. As in higher organisms the information.
Salmonella typhimurium encodes an SdiA homolog a. A process of cell-cell communication in bacteria Autoinducers. Small molecules secreted by bacteria that are used to measure population density AHL.
This creates a positive feedback loop that causes the entire population to switch into quorum-sensing mode and produce light. Bacteria primitive single-celled organisms communicate with chemical languages that allow them to synchronize their behavior and thereby act as enormous multi-cellular organisms. This process is called quorum sensing and it enables bacteria to successfully infect and cause disease in plants animals and humans.
Investigations of the molecular mechanisms underlying quorum sensing are leading to the. Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. In a process called quorum sensing groups of bacteria communicate with one another to coordinate their behavior and function like a multicellular organism.
A diverse array of secreted chemical signal molecules and signal detection apparatuses facilitate highly productive intra- and interspecies rel. One type of bacterial cell-cell communication is referred to as quorum sensing. Quorum sensing-controlled behaviors are those that only occur when bacteria are at high cell population densities.
These behaviors are ones that are unproductive when undertaken by an individual bacterium but become effective by the simultaneous action of a group of cells. For example quorum sensing regulates. An individual bacterial cell is able to sense other members of the same species and in response differentially expresses specific genes.
Such cell to cell communication is called quorum sensing QS and involves the direct or indirect activation of a response regulator by a signal molecule. Bacteria use multiple quorum-sensing autoinducers for communication in complex environments composed of many bacterial species which is the normal situation in your intestine mouth skin and other environments. They decode these chemical blends to distinguish self from other and we think in so doing they discern friend from potential foe.
This capability allows bacteria to form teams with the. Within the biofilm the bacteria use cell-to-cell communication systems to pool their activities and act in a multicellular organized manner. One such activity is to launch their arsenal of virulence factors at the strategically right moment and hence coordinate the progressive attack on the host.
This process is termed quorum sensing QS whereby bacteria produce diffusible chemical signals. Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Bacteria communicate with one another using chemical signal molecules.
As in higher organisms the information supplied by these molecules is critical for synchronizing the activities of large groups of cells. Quorum Sensing or quorum signalling is the ability to detect and respond to cell population density by gene regulation. As one example quorum sensing QS.
Quorum sensing bacteria produce and release chemical signal molecules called autoinducers that increase in concentration as a function of cell density. The detection of a minimal threshold stimulatory concentration of an autoinducer leads to an alteration in gene expression. Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria use quorum sensing communication circuits to regulate a diverse array of.
Quorum sensing QS is a bacterial cell-to-cell signaling system that controls the production of virulence factors in many pathological bacteria 9697. QS is mediated by the production of autoinducers small signal molecules that activate or repress gene expression when a minimal threshold concentration is reached 9697. Quorum sensing is a mechanism of cell to cell signaling or density sensing in micro-organisms.
Characteristics for quorum sensing For the bacteria to use quorum sensing constitutively they must possess three characteristics. To secrete a signaling molecule an auto-inducer. Bacteria can monitor and respond to changes to environmental conditions via a cell density process known as quorum sensing QS.
Bacteria uses this process to monitor their community by producing detecting and responding to low molecular mass signal molecules called autoinducers AI. Waters CM Bassler BL. Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria.
Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21. PubMed CrossRef Google Scholar.