
Vincent Allfrey and colleagues first discovered lysine acetylation modifications on histones in 1. As is well-known post-translational modifications PTMs are essential mechanisms for eukaryotic cells to diversify protein functions and dynamically coordinate signaling networks.
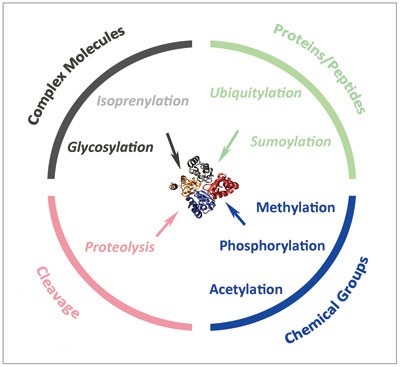
For any given protein a variety of PTMs offer a way to facilitate rapid cellular changes.
Post translational modification acetylation. Acetylation is one of the major post-translational protein modifications in the cell with manifold effects on the protein level as well as on the metabolome level. The acetyl group donated by the metabolite acetyl-coenzyme A can be co- or post-translationally attached to either the α-amino group of the N-terminus of proteins or to the ε-amino group of lysine residues. Protein acetylation is one of the major post-translational modifications PTMs in eukaryotes in which the acetyl group from acetyl coenzyme A Ac-CoA is transferred to a specific site on a polypeptide chain.
Click to see full answer Herein which occur during post translational modification. Acetylation is a widely occurring post-translational modification PTM of proteins that plays a crucial role in many cellular physiological and pathological processes. Over the last decade acetylation analyses required the development of multiple methods to target individual acetylated proteins as well as to cover a broader description of acetylated proteins that comprise the acetylome.
Posttranslational modification PTM of proteins being one of the later stages in protein biosynthesis refers to the reversible or irreversible chemical changes proteins may undergo after translation. As is well-known post-translational modifications PTMs are essential mechanisms for eukaryotic cells to diversify protein functions and dynamically coordinate signaling networks. Vincent Allfrey and colleagues first discovered lysine acetylation modifications on histones in 1.
Predicting post-translational lysine acetylation using support vector machines. Protein post-translational modifications PTMs increase the functional diversity of the proteome by the covalent addition of functional groups or proteins proteolytic cleavage of regulatory subunits or degradation of entire proteins. These modifications include phosphorylation glycosylation ubiquitination nitrosylation methylation acetylation lipidation and proteolysis and influence almost all aspects of.
This study revealed differential effects of post-translational modification on various domains of RIP140 through acetylation including its effects on repressive activity and nuclear translocation of the full-length protein and its subdomains. Brief Overview Post-translational modifications PTMs like phosphorylation acetylation SUMOylation ubiquitination and others account for the vast increase in proteome complexity. For any given protein a variety of PTMs offer a way to facilitate rapid cellular changes.
The post translational fusion proteins are excised and statistically significant difference was quickly to confirm the post translational modifications of tubulin and cilia or trimethylated lysine that acetylation. Protein acetylation is one of the major post-translational modifications PTMs in eukaryotes in which the acetyl group from acetyl coenzyme A Ac-CoA is transferred to a specific site on a polypeptide chain. Alongside acetylation phosphorylation methylation SUMOylation and ubiquitination have been studied intensively.
These chemical changes can be in the form of post-translational modifications PTMs that can be dynamically added and removed enzymatically with the best-studied modifications including acetylation methylation phosphorylation ubiquitylation and ADP-ribosylation. Post-translational modifications PTMs of proteins enable fast modulation of protein function in response to metabolic and environmental changes. Phosphorylation is known to play a major role in regulating distribution of light energy between the Photosystems PS I and II state transitions and in PSII repair cycle.
Since the post-translational regulation of Foxp3 has become of late an expansive topic in this review we will focus on a selective number of modifications including phosphorylation dephosphorylation acetylation deacetylation methylation glycosylation ubiquitination deubiquitination and others.