
Up to 60 of the human adult body is water. Why is water necessary for life.
Water as an essential nutrient.
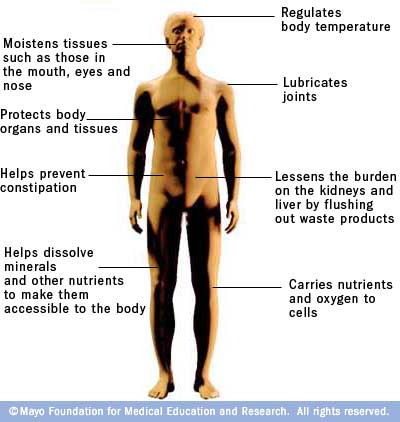
Physiological role of water. Water consumption helps lubricate and cushion your joints spinal cord and tissues. This will help you enjoy physical activity and lessen discomfort caused by conditions like arthritis. Biological Roles of Water.
Why is water necessary for life. The Molecular Make-up of Water. Many of waters roles in supporting life are due to its molecular structure and a few.
Water is the Universal Solvent. As a polar molecule water interacts best with other polar molecules such as itself. Water is of major importance to all living things.
In some organisms up to 90 of their body weight comes from water. Up to 60 of the human adult body is water. Mitchell Journal of Biological Chemistry 158 the brain and heart are composed of 73 water and the lungs are about 83 water.
Functions of water in the body. Nearly all of the major systems in your body depend on water. Water temperature plays an integral role in emotional health as well.
Connie Hernandez and Dr. Marcel Hernandez of Pacific Naturopathic in Mountain View California cool water. In the end the final and precise regulation of water balance is dependent on thirst and on ADH release with its predominant role in water reabsorption in the kidneys.
Water protects the cells from temperature fluctuations. Water is an essential abiological component of the ecosystem. Due to the high heat capacity water prevents the effects of temperature fluctuations in the surroundings.
Water has high density than air this ensures precipitation and raining. Water affects intensely many physical and chemical reactions of the soil as well as plant growth. The properties of water can be explained by the structure of its molecule.
Two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen combine to form a molelargely determined by that of the oxygen ion. The two hydrogen ions take up practically no space. Water composing almost 65 of the body is a fundamental element for human metabolism.
It has the ability to control various metabolic processes such as organising blood volume temperature of body and muscle contractions. The aim of this review is to describe the physiology of water balance and consequently to highlight the new recommendations with regard to water requirements. Water has numerous roles in th.
Water as an essential nutrient. The physiological basis of hydration. ADH signals the kidneys to recover water from urine effectively diluting the blood plasma.
To conserve water the hypothalamus of a dehydrated person also sends signals via the sympathetic nervous system to the salivary glands in the mouth. Water has a high specific heat capacity meaning that it needs to gain a lot of energy to raise its temperature. Conversely it also needs to lose a lot of energy to lower its temperature.
Waters specific heat capacity is 42 kJg o C. Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation which means a lot of energy is required to evaporate it. When it evaporates water draws thermal energy out of the surface its on.
Water has numerous roles in the human body. It acts as a building material. As a solvent reaction medium and reactant.
As a carrier for nutrients and waste products. And as a lubricant and shock absorber. In drylands where water is the most limiting factor Ji et al 2013 Kidron 2014 Noy-Meir 1973 water availability dominates the physiological activity of poikilohydric BSCs organisms.
Therefore water is a crucial factor in the growth and development of BSCs Jia et al 2014. Insight into the physiological role of water absorption via the leaf surface from a rehydration kinetics perspective 2018 GuzmánDelgado Paula. Along with other important physiological parameters such as pH bile salts gastric emptying rate and motility water content in the gastrointestinal tract has the potential to influence greatly.
