
Viral hemorrhagic fevers VHFs are a group of zoonotic diseases characterized by fever and bleeding disorders that can progress to shock and death. The distribution of bovine viral diarrhoea virus BVDV antigen in tissues of animals with acute and chronic bovine viral diarrhoea-mucosal disease BVD-MD was examined using improved indirect immunofluorescence and.
The distribution of bovine viral diarrhoea virus BVDV antigen in tissues of animals with acute and chronic bovine viral diarrhoea-mucosal disease BVD-MD was examined using improved indirect immunofluorescence and.
Pathogenesis of viral diseases. Pathogenesis is the process by which an infection leads to disease. Pathogenic mechanisms of viral disease include 1 implantation of virus at the portal of entry 2 local replication 3 spread to target organs disease sites and 4 spread to sites of shedding of virus into the environment. Interest in viral pathogenesis stems from the desire to treat or eliminate viral diseases that affect humans.
This goal is achieved in part by identifying the viral and host genes that influence the production of disease. Progress in understanding the molecular basis of viral pathogenesis comes largely from studies of animal models. Viral pathogenesis is the process by which viruses produce disease in the host.
The factors that determine the viral transmission multiplication dissemination and development of disease in the host involve complex and dynamic interactions between the virus and the susceptible host. Viral infection is not synonymous with disease as many viral infections are subclinical syn asymptomatic inapparent whereas others result in disease of varying severity that is typically accompanied by characteristic clinical signs in the affected host Amongst many other potentially contributing factors the outcome of the virushost encounter is essentially the product of the. Pathogenesis and Control of Viral Diseases Interferons are an important part of the host defense against viral infections.
What is interferons principal mode of action. A It is present in the serum of healthy individuals providing a viral surveillance role. Pathology of viral disease Ila R.
March 21 2003 6 Methods of diagnosis for viral diseases Serology Cytology or Histology Viral growth in cell culture Detection of viral genome I. Serology Look for viral antigens or anti-viral antibodies A four fold or greater rise in titer between two serum specimens provides a positive diagnosis. A The virus or viral component - complement - antibody complex is fixed to a cell usually an erythrocyte or leukocyte or platelet resulting in complement-dependent cell lysis.
This is the pathogenic mechanism in many viral diseases where anemia is one of the clinical manifestations. Research programs in the Laboratory of Viral Diseases LVD explore fundamental aspects of cell and molecular biology viral pathogenesis and viral immunology within the context of a diverse group of medically important viruses that includes humansimian immunodeficiency viruses poxviruses herpesviruses papillomaviruses coronaviruses influenza viruses alphaviruses and flaviviruses. The first step in COVID-19 pathogenesis is viral invasion via its target host cell receptors.
SARS-CoV-2 viral entry has been described in detail elsewhere. In brief SARS-CoV-2 consists of four main structural glycoproteins. Spike S membrane M envelope E and nucleocapsid N.
Pathogenesis of bovine viral diarrhoea-mucosal disease. Distribution and significance of BVDV antigen in diseased calves. The distribution of bovine viral diarrhoea virus BVDV antigen in tissues of animals with acute and chronic bovine viral diarrhoea-mucosal disease BVD-MD was examined using improved indirect immunofluorescence and.
The Viral Pathogenesis Research Laboratory is interested in the host cellular response to viral infection and identification of genes and signalling pathways that are induced in an attempt to control viral replication in particular hepatitis C dengue and Zika virus. Her primary research interest is in the pathology and pathogenesis of emerging infectious diseases with particular interest in viral hemorrhagic fevers. Ritter is a pathologist with the Division of High-Consequence Pathogens and Pathology National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases CDC Atlanta.
Emerging and well-known viral diseases remain one the most important global public health threats. A better understanding of their pathogenesis and mechanisms of transmission requires animal models that accurately reproduce these aspects of the disease. Here we review the role of ferrets as an animal model for the pathogenesis of.
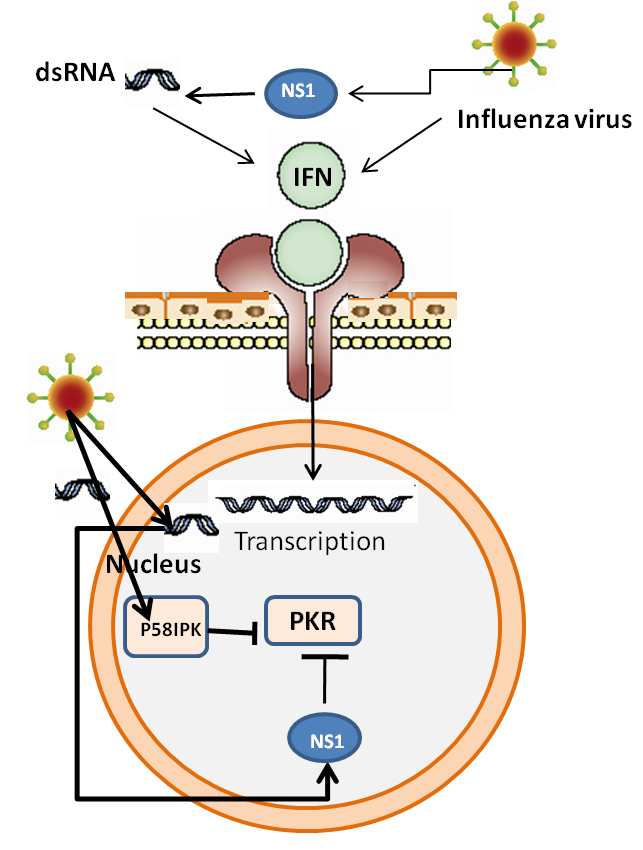
The goal of the Viral Pathogenesis Laboratory VPL in the Vaccine Research Center VRC is to better understand basic aspects of viral pathogenesis and apply that knowledge toward development of safer and more effective vaccines. Many aspects of prior VPL work were instrumental in the rapid response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The pathogenesis of influenza virus infection depends on viral virulence and host responses 63.
Host responses will be discussed in the next section. The crucial site for influenza virus infection that leads to severe pneumonia is the alveolar epithelium 64. The purpose of this project is to follow the pathogenesis of avian viral pathogens in commercial poultry in order to determine where they might be controlled and to develop new methods to prevent losses from these diseases.
One of the diseases. Pathogenesis of acute viral disease induced in fish by carp interstitial nephritis and gill necrosis virus. A lethal disease of koi and common carp species Cyprinus carpio has afflicted many fish farms worldwide since 1998 causing severe financial losses.
This emphasises that viral load may drive these cytokines and the possible pathological roles associated with the host defence factors. This is in keeping with the pathogenesis of influenza SARS and MERS whereby prolonged viral shedding was also associated with severity of illness7 35. Viral hemorrhagic fevers VHFs are a group of zoonotic diseases characterized by fever and bleeding disorders that can progress to shock and death.
They are caused by different groups of viruses from the families Flaviviridae Bunyaviridae Arenaviridae and Filoviridae.