
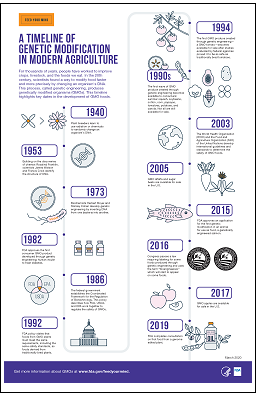
2015 FDA approves an application for the first genetic modification in an animal for use as food a genetically engineered salmon. Genetically Modified Food The First GM Food.
GMO Timeline A History of Genetically Modified Foods.
Origin of genetically modified foods. 2015 FDA approves an application for the first genetic modification in an animal for use as food a genetically engineered salmon. 2016 Congress passes a law requiring labeling for some foods. A 1980 court case between a genetics engineer at General Electric and the US.
Patent Office is settled by a 5-to-4 Supreme Court ruling allowing for the first patent on a living organism. The GMO in question is a bacterium with an appetite for crude oil ready to gobble up spills. 1982 - FDA Approves First GMO.
GMO Timeline A History of Genetically Modified Foods. As originally seen on Rosebud Magazine 2012 with sources added by GMO-Awareness. GMO foods are such an embedded part of our food system these days but its not difficult to think back to a time when food was simpler and healthier.
How did we get to the point that genetically modified. Genetically Modified Food The First GM Food. In the early 1990s Calgene Inc.
Developed the worlds first genetically modified GM food. In the 1990s Hawaiis rainbow papaya production fell 40 due to the ringspot virus which. The Real GMO.
History of genetically modified food. The first commercially grown genetically modified food crop was a tomato created by California company in the early 1990s. Called the FlavrSavr it was.
Genetically Modified Foods GMF are produced from organisms that have had their genes altered to introduce traits not created through natural selection. In 1983 Monsanto scientists were some of the first to genetically modify plants and five years later they tested their first genetically engineered crops. Scientists inserted genes into soybeans ultimately creating what would become the most common GMO.
Making a crop that was resistant to herbicide made it much easier and cheaper for. Food ingredients derived from genetically modified plants intended for human consumption OECD 1993. This concept embodies a science-based approach in which a genetically modified food is compared to its existing appropriate counterpart.
The approach is not intended to establish absolute safety which is an unattainable goal for any food. In 2011 genetically modified corn one of the examples of genetically modified foods with full explanations was grown in 14 countries. GM corn comes in several varieties herbicide-resistant.
The first genetically modified food animal approved for sale is salmon. Commercial sale of genetically modified food began in 1994 when Calgene first marketed its delayed ripening tomato. Genetically modified foods include.
Soybean corn canola rice and cotton seed oil. Genetic modification allows just one individual gene or a small number of genes to be inserted into a plant or animal. This enables them to be used.
Salmon is the first genetically modified animal to enter the food supply. The salmon are engineered to grow to full adult size about twice as fast as they normally would. Avoid eating processed foods containing salmon.
Modern biotechnology is trying to create new genetically modified GM foods that express useful traits such as insect resistance herbicide tolerance infectious-agent resistance and resistance to environmental changes. The traceability of GM organisms GMOs is ensured through the use of strategies and regulations based on molecular detection methods. These methods can be categorized as indirect eg immunologic or direct eg genetic.
An experiment conducted by a British biochemist on the safety of genetically modified foods found that when mice ate genetically modified potatoes the stomach wall thickened and gastric glands grew which means that the risk of cancer may increase. Studies have also found that this will reduce the immunity of mice and even their resistance to diseases. The Commission Directive EU 2018350 of 8 March 2018 amending Directive 200118EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the environmental risk assessment of genetically modified organisms was published on 9 March 2018.
This measure brings the requirements on ERA up to date with developments in scientific knowledge and technical progress while building on the EFSA.