
The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. There is an upper and lower epidermis in the leaves.
The epidermis in plants is a layer of cells that usually covers the roots stems leaves and flowers of plants.
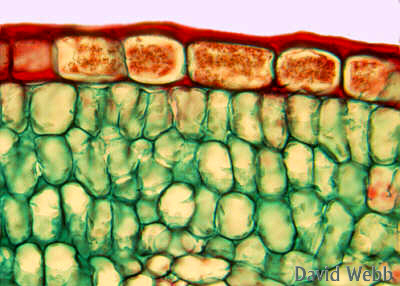
Multiple epidermis plants examples. The protoderm cells divide anticlinally and in course of time uniseriate epidermis is formed. Many-layered or multiseriate epidermis usually called multiple epidermis is found in some organs like roots of orchids leaves of Ficus spp. 507A Nerium Peperomia etc.
Məltəpəl epədərməs botany Epidermis that is several layers thick occurring in many species of Ficus Begonia and Peperomia. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific Technical Terms 6E Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. Want to thank TFD for its existence.
Epidermis in botany outermost protoderm-derived layer of cells covering the stem root leaf flower fruit and seed parts of a plant. The epidermis and its waxy cuticle provide a protective barrier against mechanical injury water loss and infection. Various modified epidermal cells regulate.
Like the skin epidermis the epidermis of the plant covers the outer surface and thus covers all plant tissue from the roots to the tip. Made up of epidermal cells the epidermis in plants also serves as a protective layer that not only prevents various microorganisms from gaining entrance into the underlying tissue of leaves and stems but also prevents excess water loss among a few other functions. The Velamen of orchid roots is another example of a multiple epidermis.
The cells are dead at maturity and can store free water. This is important for epiphytes because their roots may be directly exposed to the atmosphere. There is an Endodermal-like layer between the Velamen and the living parenchyma of the root.
This suggests that the root in a manner similar to that which occurs at the Endodermis which. Vallisneria Hydrilla Eichhornia water hyacinth Wolffia Lemna etc. Aquatic environment provides a matrix for plant growth in which temperature fluctuation is at minimum and the nutrients occur mostly in dissolved state but light and oxygen become deficient with the increase m.
Epidermis in roots. The epidermis in the roots of a plant is the outside layer of a root. Its function is to protect the rootEpidermis in leaves.
There is an upper and lower epidermis in the leaves. The outer layer of cells of the stems roots and leaves of plants. In most plants the epidermis is a single layer of cells set close together to protect the plant from water loss invasion by fungi and physical damage.
The epidermis that is exposed to air is covered with a protective substance called cuticle. Dwi two Sahkoshik. In this type of stoma there are two subsidiary cells each of which is situated laterally on either side of the pair of guard cells.
Chatus four Sahkoshik. For example the inhibition of cell division in the epidermis by expression of the cell cycle inhibitor Kinase Inhibitor Protein KIPRELATED PROTEIN1INHIBITOR1 OF CDC2 KINASE KRP1ICK1 under the control of the AtML1 promoter Bemis Torii 2007 resulted in small plants which had abnormally large epidermal cells. Surprisingly cell division frequency in the mesophyll of these plants was not.
Role of epidermis in plants. Protection of the underlying cells and tissues. Prevention of water loss.
Prevention of mechanical injury and invasion by parasite fungi. Exchange of gases and transpiration through stomata. This is an answered question from Chapter 6.
Tissues of CBSE Class 9th Science. Trichomes on plants are epidermal outgrowths of various kinds. The terms emergences or prickles refer to outgrowths that involve more than the epidermis.
This distinction is not always easily applied see Wait-a-minute tree. Also there are nontrichomatous epidermal cells that protrude from the surface. Example needed A common type of trichome is a hair.
The epidermis in plants is a layer of cells that usually covers the roots stems leaves and flowers of plants. The epidermis is 4 layers thick and are as follows- stratum basale stratum corneum stratum granulosum stratum spinosum. The role of the epidermis in plants are as follows.
Provides protection against water loss. Proportions of epidermis from different species in the faeces. And 3 a comparison of the proportions of epidermis in the faeces with the proportions of the different species ingested.
Information was also obtained concerning the survival during digestion of epidermis from one or both leaf surfaces the interval between first ingestion of a plant. Among plants the whole order Brassicales from rosids is capable to produce myrosinase examples are different cabbages Brassica spp papaya Carica horseradish tree Moringa. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly.
The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium particularly a stratified squamous epithelium The word epidermis is derived through Latin from Ancient Greek epidermis itself from Ancient Greek. A leaf is composed of more than one type of cell therefore is an organ tissues only contain one type of cell For example epidermal cells spongey mesophyll cells etc.
A leaf also performs various functions eg. Transpiration photosynthesis protein synthesis while a tissue performs only a specific function.