Sunlight air precipitation minerals and soil are some examples of abiotic factors. Water - The makeup of the water how it moves and how available it is.
In terrestrial ecosystems physical conditions in the atmosphere at the surface and within the soils all interact to create the conditions that give rise to vegetation that develops.
Measuring abiotic factors in an ecosystem. Meteorological equipment can be used to measure weather and climate conditions. Direct chemical tests are used to measure chemical pollutant levels to give us an indication about the concentration of pollutants. Examples of direct chemical tests would include.
Water tested for PH levels and samples can be assessed for metal ion content eg. Measuring the pH and moisture of the soil Soil moisture and soil pH meters are used by simply pushing the probe into the soil and reading the meter. Errors can be made when measuring abiotic.
Measuring abiotic components. Ecosystem can divvied into 3 types. Marine sea estuaries salt marches and mangroves.
Freshwater rivers lakes and wetlands. Each ecosystem has its own specific abiotic factors. Abiotic factors of marine ecosystem.
Abiotic factors can all be measured to show the living conditions in an ecosystem. Light meters can be used to measure light intensity. Techniques for measuring abiotic factors.
Non-living factors can be measured through data loggers expensive chemical testing equipment simple thermometers and observations. As you are reading this webpage consider how you may record this data efficiently and accurately in the field. Theres a wide variety of abiotic factors that influence what may live in an ecosystem some examples of which are listed below.
Salinity - many marine organisms tolerate a variety of salt concentration levels in the water which can be checked with a few tools. Hydrometer measures specific gravity or density of a sample relative weight of 10L salt water compared to 10L pure fresh water refractometer measures. There are five main abiotic factors that are important to all ecosystems.
The amount and type of each abiotic factor determines what life can survive in that ecosystem. Water - The makeup of the water how it moves and how available it is. Sunlight - The amount and intensity of regular sunlight exposure.
To a large extent it is the physical abiotic conditions within any environment that controls the plant and thus the animal biotic community that develops. In terrestrial ecosystems physical conditions in the atmosphere at the surface and within the soils all interact to create the conditions that give rise to vegetation that develops. Abiotic Biotic Factors in Ecosystems Sciencing The interrelated abiotic and biotic factors in an ecosystem combine to form a biome.
Abiotic factors are the nonliving elements like air water soil and temperature. Biotic factors are all the living elements of the ecosystem including the plants animals fungi protists and bacteria. Measuring abiotic component Three types of Ecosystems.
Freshwater Rivers lakes and wetlands 3. Terrestrial Land-Based Abiotic factors of a Marine ecosystem. Abiotic factors of a Freshwater ecosystem.
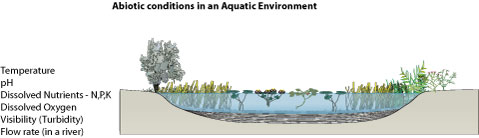
Know the methods for measuring any three significant abiotic factors and how these may vary in a given ecosystem with depth time or distance. Marinesalinity pH temperature dissolved oxygen wave action. Freshwaterturbidity flow velocity pH temperature dissolved oxygen.
A concise description of Abiotic factors in an ecosystem and examples. The abiotic or non-living factors in an ecosystem include. Temperature turbidity pH dissolved oxygen nitrate levels and phosphate levels.
These non-living factors can have considerable impact on freshwater ecosystems particularly if they impact on autotrophic organisms also known as producers. Measurements in ecosystems Ecosystems involve the interaction between abiotic non-living and biotic living parts of the environment. It is vital to find which factors need to be measured in a habitat.
For example Rainfall contributes to tropical rainforest ecosystems sand in desert ecosystems and water salinity ocean currents pressure in the marine ecosystem. All the factors are interrelated to each other. All the biotic components ie living components are directly or indirectly dependent upon the abiotic factors.
Abiotic factors refer to all the non-living ie. Chemical and physical factors present in the atmosphere hydrosphere and lithosphere. Sunlight air precipitation minerals and soil are some examples of abiotic factors.
These factors have a significant impact on the survival and reproduction of species in an ecosystem. Lesson 1 Abiotic and Biotic Factors in Ecosystems Ecosystems An ecosystem is made up of all the organisms in an area and their relationships with each other and with. PowerPoint PPT presentation.