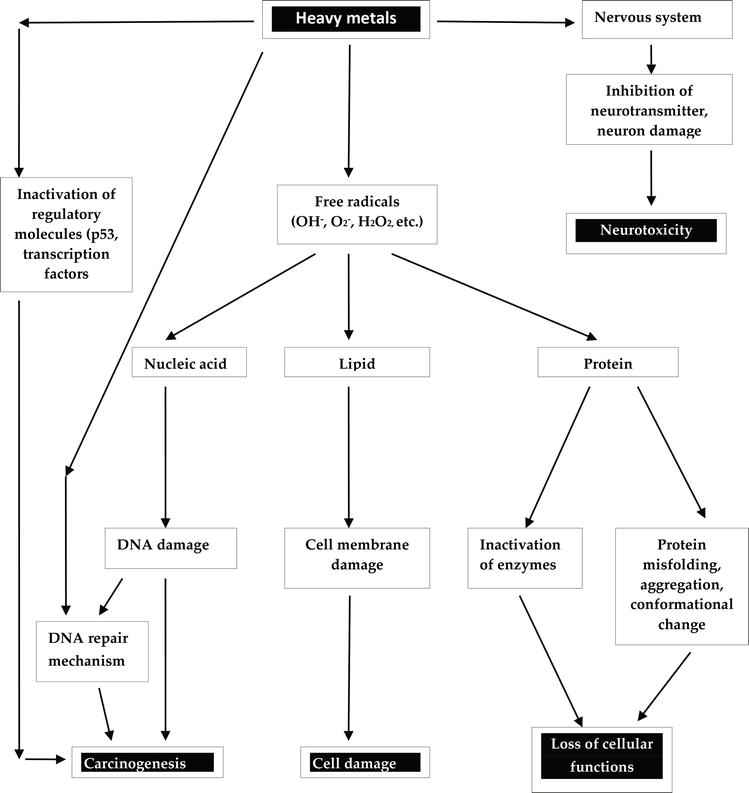
Furthermore the impact of heavy metals in the body may induce degenerative symptoms and clinical studies have shown a strong correlation between metal exposure and neurological diseases. Heavy metals eg Cr Cu and Zn in soil can cause non-carcinogenic human health hazards such as neurologic complications headaches and liver disease US EPA 2000.

Are associated to different degrees with a wide range of conditions including kidney and bone damage developmental and neuro-behavioral disorders elevated blood pressure and potentially even lung cancer.
Impact of heavy metals on human health. The main threats to human health from heavy metals are associated with exposure to lead cadmium mercury and arsenic. These metals have been extensively studied and their effects on human health regularly reviewed by international bodies such as the WHO. Heavy metals have been used by humans for thousands of years.
Largest human-caused source of mercury emissions to the air in the United States. Mercury in soil and water is converted by microorganisms to methylmercury a bioaccumulating toxin. Health effects The EPA has determined that mercuric chloride and methylmercury are possible human carcinogens.
The nervous system is very sensitive to all forms of. Heavy metal toxicity has proven to be a major threat and there are several health risks associated with it. The toxic effects of these metals even though they do not have any biological role remain present in some or the other form harmful for the human body and its proper functioning.
Following exposure to heavy metals their metabolism and subsequent excretion from the body depends on the presence of antioxidants glutathione α-tocopherol ascorbate etc associated with the quenching of free radicals by suspending the activity of enzymes catalase peroxidase and superoxide dismutase. Effects on human health Humans are exposed to cadmium by inhalation and ingestion although the main health impacts recorded in the literature are through dietary exposure kidney and bone damage and inhalation from smoking tobacco and occupational exposure lung damage. Dietary intake accounts for 90 of all exposure in non-smokers.
There are 23 heavy metals that are of concern to the health of humans. Antimony arsenic bismuth cadmium cerium chromium cobalt copper gallium gold iron lead manganese mercury nickel platinum silver tellurium thallium tin uranium vanadium and zinc. Heavy metal toxicity can lower energy levels and damage the functioning of the brain lungs kidney liver blood composition and other important organs.
As long ago as 2007 the World Health Organization stated that heavy metals accumulated in the environment. Are associated to different degrees with a wide range of conditions including kidney and bone damage developmental and neuro-behavioral disorders elevated blood pressure and potentially even lung cancer. From a therapeutic viewpoint considerable re- of the known metals and metalloids are very toxic to living search and development efforts are being exerted to decorpo- organisms and even those considered as essential can be rate metal ions from the body.
Since the use of As in World toxic if present in excess. Effects of heavy metal ingestion as the THQ va lue of children and adults was 541 and 412 respectively. The risk of human health by heavy metals Fe As Cr Mn Cu.
9 rows Several heavy metals are found naturally in the earth crust and are exploited for various. Furthermore the impact of heavy metals in the body may induce degenerative symptoms and clinical studies have shown a strong correlation between metal exposure and neurological diseases. Although toxicity and the resulting thre at to human health of any contaminant are of course a function of concentration it is well-known that chronic exposure to heavy metals and metalloids at.
Exposure to heavy metals can cause various serious human diseases such as respiratory problems kidney pathology neurological disorders and cancers. For example chromium is carcinogenic and can provoke skin lesions and respiratory problems Mohammadi et al. Heavy metals eg Cr Cu and Zn in soil can cause non-carcinogenic human health hazards such as neurologic complications headaches and liver disease US EPA 2000.
Liu et al 2013. Cr VI is more hazardous than Cr III and other ionic forms in terms of its stability. Exposure to multiple heavy metals can have synergistic or antigonistic effects on human health.
As in ground water has become a global issue. In many cases the co-presence of As Mn and Sb in drinking water has been reported. Co-exposure of As with other heavy metals eg Sb and.
Ingestion of vegetables containing heavy metals is one of the main ways in which these elements enter the human body. Once entered heavy metals are deposited in bone and fat tissues overlapping noble minerals. Slowly released into the body heavy metals can cause an array of diseases.