
May mean the physical characters such as grain size colour taste flavour odour and texture or chemical compositions that attributes to these and other nutritional and. As an applied science breeders are offered opportunities to apply principles and technologies from several.
Plants can be bred to improve quality and to meet consumer preferences which leads to a reduction in food loss and waste.
Goals of plant breeding. Plant Breeding and its Goals Goals. The plant breeder usually has in mind an ideal plant that combines a maximum number of desirable characteristics. One of the aims of virtually every breeding project is to increase yield.
The Goals Of Modern Plant Breeding. The broad aims of current plant breeding programs have changed little from those of the past. Improvements in yield quality plant hardiness and pest resistance are actively being sought.
In addition the ability of plants to survive increasing intensities of ultraviolet radiation due to damage in the ozone. But plant breeding is not just about addressing environmental challenges. Plants can be bred to improve quality and to meet consumer preferences which leads to a reduction in food loss and waste.
6 Most Important Objectives of Plant Breeding 1. Plants are the main source of food for man either directly or indirectly. The quality of plants in terms of height size or.
Plant breeding aims to improve the characteristics of plants so that they become more desirable agronomically and economically. The specific objectives may vary greatly depending. The most common goal of crop breeding is the improve the genetic performance of plants.
As plants are the principal producer of food for the planet as well as fundamental components of medicine clothes and raw materials the primary performance goal. In plant breeders the aim is to improve the characteristics of plants to make them more desirable agronomical and economically. Is the ultimate goal of all plant breeding programs.
May mean the physical characters such as grain size colour taste flavour odour and texture or chemical compositions that attributes to these and other nutritional and. Traits in the breeding goal were. Mature weig ht an d feed re qui remen ts of so ws.
Lo nge vity of sows. Gro wth rate and daily feed intake of. The NAPB works to help create a future in which 1 Strong public and private sectors work independently and together to deliver varieties and improved germplasm to society 2 The value and importance of plant breeding to food security quality of life and a sustainable future are known and appreciated by the public and 3 Plant breeding is viewed as dynamic problem solving and creative.
Development of crop varieties suitable for mechanized agriculture has become a major goal of plant breeding in recent years. Uniformity of plant characters is very important in mechanized agriculture because field operations are much easier when the individuals of a variety are similar in time of germination growth rate size of fruit and so on. Document the contribution of plant breeding to the public good in terms of the environment climate change food security economic growth and health that can be used to garner public support for plant breeding.
Initiate the development of a coherent national plan for plant breeding. What are the 3 goals of plant breeding. Who was the first animal and plant bree.
When you cross two things you always have one that shows itself. The use of tools and techniques for the selection of desirable. 2 identify superior plants.
Following are the major objectives of plant breeding. To increase the crop yield. To raise plants with desired characteristics.
To develop a disease-resistant crop. To develop plants that can tolerate extreme environmental stress. Guide Plant Breeding Technician IT.
Setting up a work space. Working with small grains. Using plant breeding software.
Cultivation properties Another plant breeding objective is to breed plants for adaptation to agronomic production processes. This mainly requires properties such as lodging height winter hardiness maturation period and steady growth. Modern plant breeding is a discipline that is firmly rooted in the science of genetics.
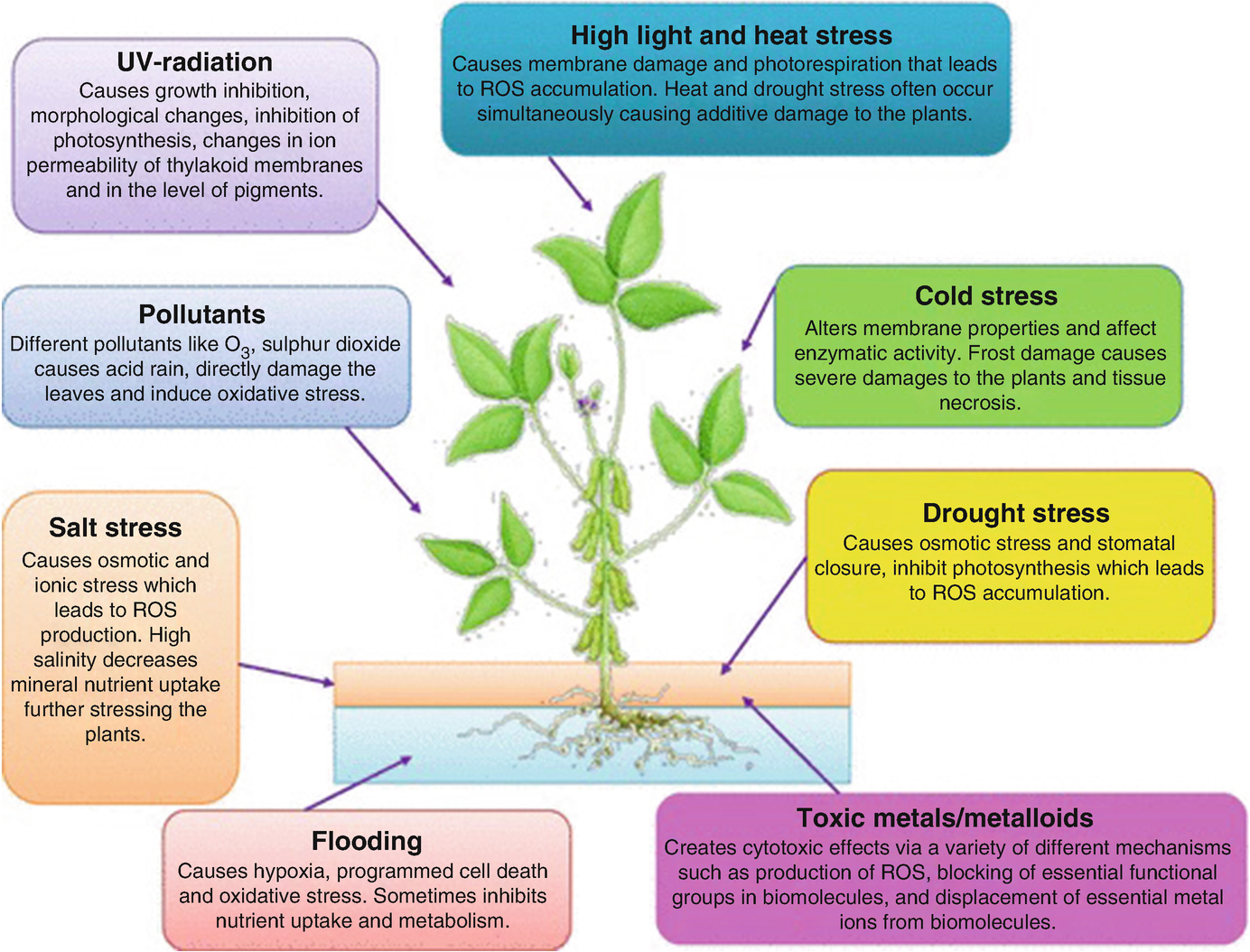
As an applied science breeders are offered opportunities to apply principles and technologies from several. Plants are subject to various environmental influences that have significant effects on yield stability. High resistance to pests and plant diseases but also an increased tolerance for environmental factors such as drought and cold are key goals of plant breeders.
Climate change also keeps posing new challenges that must be overcome.