Erythropoietin Epo is the principal regulator of erythropoiesis by inhibiting apoptosis and by stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of erythroid precursor cells. Oxygen-regulated transcription of the.

Answered Jul 27 2018 by NetworkHinch.
Erythropoietin is produced by. Erythropoietin is produced by Erythropoietin is produced and released by. Proximal tubular cells C. Peritubular capillary lining cells of kidney D.
All of the above. The correct answer is C. Peritubular capillary lining cells of kidney.
Physiologic regulator of RBC production glycoprotein hormone EPO is produced released by highly specialized epithelial-like. Erythropoietin is produced by the kidneys specifically by the interstitial fibroblasts in close association with the peritubular capillary and the proximal convoluted tubule. Interestingly erythropoietin is also produced by the liver during the fetal and perinatal period by the perisinusoidal cells.
Erythropoietin Epo is a glycoprotein that promotes the proliferation and differentiation of erythrocyte precursors. The major site of Epo production is the kidney while the liver is the main extrarenal site of Epo production. Within these organs the cells synthesizing Epo were identified by usin.
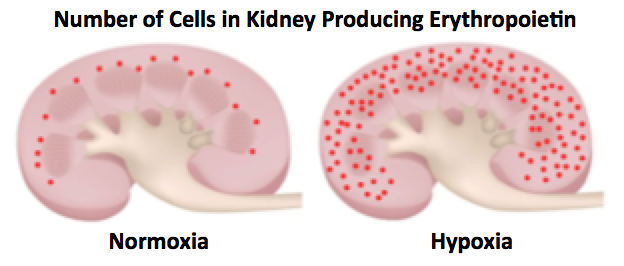
Within the kidney erythropoietin is produced by interstitial fibroblast-like cells that surround the renal tubules. When blood oxygen concentration is normal normoxia synthesis of erythropoietin occurs in scattered cells located predominantly in the inner cortex but under conditions when blood oxygen is deficient hypoxia interstitial cells within almost all zones of the kidney begin to produce the hormone. The cellular site of erythropoietin epo production within the mammalian kidney is still not completely understood.
In the present study we examined the In the present study we examined the Erythropoietin is produced by tubular cells of the rat kidney SpringerLink. Erythropoietin is produced by the kidneys to. Asked Jul 27 2018 in Anatomy Physiology by FluffyNut.
A regulate red blood cell production by the bone marrow. B regulate blood solute concentration. C conserve or eliminate hydrogen and bicarbonate ions.
D regulate removal of metabolic wastes. Answered Jul 27 2018 by NetworkHinch. Erythropoietin is distinct among the hematopoietic growth factors because it is produced primarily in the kidneys rather than the bone marrow.
The kidney functions as a critmeter in that it senses oxygen tension and extracellular volume. By regulating red cell mass through erythropoietin and plasma volume through excretion of salt and water the kidney sets the hematocrit at a normal value of 45. The kidneys and liver produce erythropoietin when oxygen levels in the cells are low.
The hormone then stimulates the bone marrow which in turn makes more red blood cells. Erythropoietin is produced by cortical nephrons in normal hematopoietic condition. Among cortical nephrons intercalated cells showed the largest Epo production.
Hypoxia induced a large increase in Epo production in peritubular cells. The hormone erythropoietin Epo maintains red blood cell mass by promoting the survival proliferation and differentiation of erythrocytic progenitors. Circulating Epo originates mainly from fibroblasts in the renal cortex.
Epo production is controlled at the transcriptional level. Erythropoietin EPO is primarily produced in the kidney. In response to hypoxia renal tubular and interstitial cells synthesize EPO and release it into blood and then EPO is distributed into various tissues through blood flow.
Oxygen-regulated transcription of the. Erythropoietin is a hormone that is produced predominantly by specialised cells in the kidney. Once it is made it acts on red blood cells to protect them against destruction.
At the same time it stimulates stem cells of the bone marrow to increase the production of red blood cells. Erythropoietin Epo is the principal regulator of erythropoiesis by inhibiting apoptosis and by stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of erythroid precursor cells. However Epo also performs extra-erythropoietic actions of which the.
Erythropoietin hormones are produced by specialised cells in the human kidney which is mainly responsible for the production of RBC- Red blood cells. Erythropoietin Stay tuned with BYJUS to learn more about erythropoietin hormones functions and other related topics. Erythropoietin regulated by Balance in erythrocyte production and destruction.
Blood levels Excessive effects and Decreased effects the Excessive effects that regulate Erythropoietin is. Erythropoietin EPO is a hormone produced by the kidney that promotes the formation of red blood cells by the bone marrow. The kidney cells that make erythropoietin are sensitive to low oxygen levels in the blood that travels through the kidney.
These cells make and release erythropoietin when the oxygen level is too low. What is Erythropoietin. Erythropoietin or EPO is a hormone that is produced by the kidney cells and stimulates the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells or RBCs.
Erythropoietin is released during hypoxemia or when the blood oxygen level is low. Erythropoietin is produced and released into the blood by the kidneys in response to low blood oxygen levels hypoxemia. Erythropoietin EPO is carried to the bone marrow where it stimulates production of red blood cells.
The hormone is active for a short period of time and then eliminated from the body in the urine.
