Pyrrole thiophene and furan are colourless liquids and boil at 130C 84C and 32C respectively. 129890 C at 760 mmHg Vapour Pressure.

Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henrys Law constant of 180X10-5 atm-cu mmole.
Boiling point of pyrrole. Pyrrole does not absorb light in the environmental UV spectrum and is not expected to directly photolyze. If released to soil pyrrole is expected to have high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 61. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henrys Law constant of 180X10-5 atm-cu mmole.
Pyrrole may potentially volatilize from dry soil. 129890 C at 760 mmHg Vapour Pressure. 12202 mmHg at 25C Enthalpy of Vaporization.
38800 kJmol Flash Point. 33300 C Index of Refraction. 0967 gmL at 25 C lit Boiling Point.
NSC 62777 Permanent link for this species. Use this link for bookmarking this species for future reference. Information on this page.
Gas phase thermochemistry data. 65 lignes T boil. Normal Boiling Point Temperature K.
In my opinion pyrrole has a higher boiling point than furan and thiophene because of two reasons. Higher dipole moment of pyrrole than furan and thiophene. Additional N-H bond in pyrrole that needs to be cleaved.
Thus pyrrole requires higher energy to overcome these two interaction forces and thus has a higher boiling point. Some of the physical constants of pyrrole and of a selection of its derivatives are collected in Table 41. The boiling point of pyrrole is higher than might have been expected and the closer similarity in this property of 1-methylpyrrole to say toluene suggests that in pyrrole the imino group is responsible for some sort of association see below.
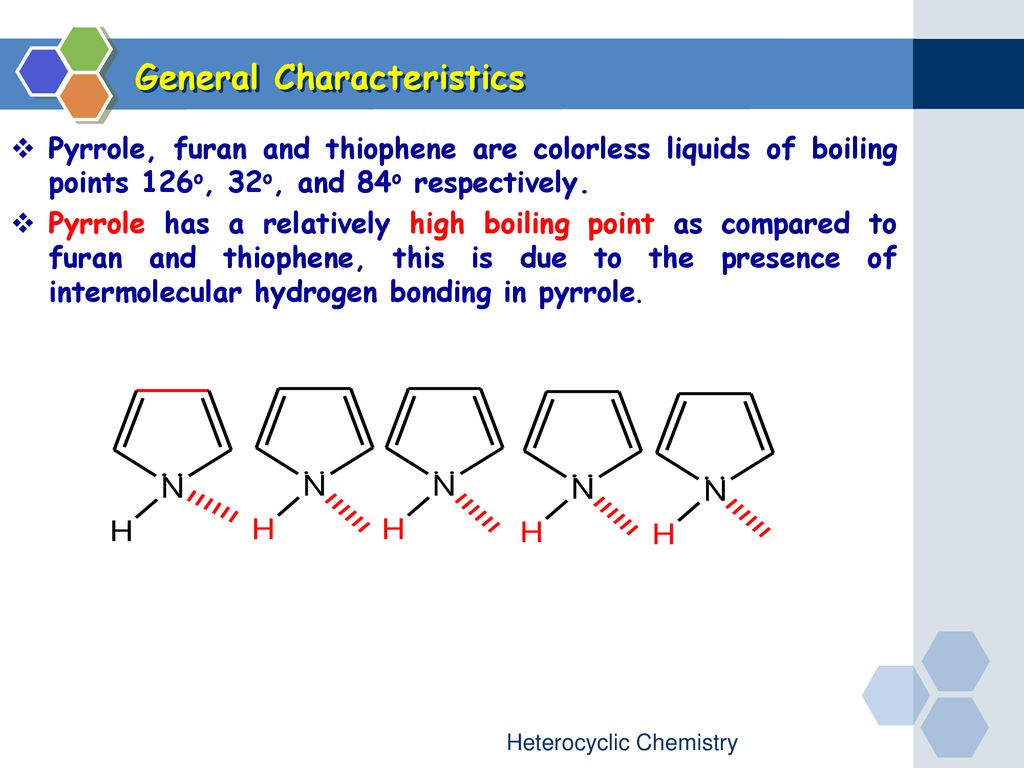
The characterization of pyrrole and simple alkylpyrroles through. General Characteristics v Pyrrole furan and thiophene are colorless liquids of boiling points 126 o 32 o and 84 o respectively. V Pyrrole has a relatively high boiling point as compared to furan and thiophene this is due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding in pyrrole.
Pyrrole pyrrolidine pyridine and 2-methylpyridine were purified to approximately 999 mole purity. Precautions necessary in the purification of these nitrogen compounds are described including protection from water and oxygen. Boiling points freezing points densities viscosities surface tensions and refractive indices were determined on each of the compounds.
Derived functions including refractivity. Pyrrole reagent grade 98 Synonym. Azole Divinylenimine Imidole CAS Number 109-97-7.
Empirical Formula Hill Notation C 4 H 5 N. Molecular Weight 6709. BeilsteinREAXYS Number 1159.
PubChem Substance ID 24848030. 2644230 C at 760 mmHg Vapour Pressure. 0012 mmHg at 25C Enthalpy of Vaporization.
58360 kJmol Flash Point. 1137226 C Index of Refraction. What is Pyrrole.
Pyrrole is a five-membered ring with the chemical formula C 4 H 4 NH. It is a heterocyclic compound in which a nitrogen atom contributes to the formation of the ring structure along with four other carbon atoms. We can observe pyrrole as a volatile and colourless liquid at room temperature.
However upon exposure to normal air the liquid readily darkens. Therefore we need to. Methyl CH 3 and ethyl C 2 H 5 groups attached to ring carbon atoms usually increase the boiling point by about 2030 C 3654 F and 5060 C 90108 F respectively whereas a similar attachment to a ring nitrogen atom eg pyrrole 1-methylpyrrole significantly decreases the boiling point because of decreased ease of intermolecular association by hydrogen bonding the active hydrogen having been.
Incorporated into the five-membered rings than six-membered rings. Pyrrole thiophene and furan are colourless liquids and boil at 130C 84C and 32C respectively. High boiling point of pyrrole is due to hydrogen bonding between pyrrole molecules.
Pyridine All six membered fully unsaturated heterocycles are related to benzene as these can be. The enthalpy of vaporization is 3509 kJmol 1 at the boiling point and normal pressure. The enthalpy of fusion is 828 kJmol 1 at the melting point.
The critical parameters of pyridine are pressure 670 MPa temperature 620 K and volume 229 cm 3 mol 1. The Koc of pyrrolidine is estimated as 42 SRC using a log Kow of 046 1 and a regression-derived equation 2. According to a classification scheme 3 this estimated Koc value suggests that pyrrolidine is expected to have very high mobility in soil.
Cordingly atmospheric pressure is preferred for commercial operation. At atmospheric pressure the boiling point of the pyrrole-water azeotrope is between about 93 and 935 0 whereas the boiling points of the water azeotropes of 3-picoline 4-pic0line and 26-lutidine are all above about 965 C.