
An E-value is the number of HSPs expected to have this score or higher purely by chance. An E-value is the number of HSPs expected to have this score or higher purely by chance.
Under Program Selection choose whether or not you want highly similar sequences or somewhat similar sequences.
Blast list all genomic databases. Catharanthus roseus aster yellows phytoplasma. Then use the BLAST button at the bottom of the page to align your sequences. To get the CDS annotation in the output use only the NCBI accession or gi number for either the query or subject.
Reformat the results and check CDS feature to display that annotation. Click Select Columns or Manage Columns. Choose a species genome to search or list all genomic BLAST databases.
The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool BLAST finds regions of local similarity between sequences. The program compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance of matches. Section we will first take a look at the common BLAST databases.
According to their content they are grouped into nucleotide and protein databases. These databases and their detailed compositions are listed in the two tables below. NCBI also provides specialized BLAST databases such as the vector screening database variety of genome databases for.
The BLAST pages offer several different databases for searching. You can select the database of your choice from the drop-down list. All data transfer from and to our database is encrypted.
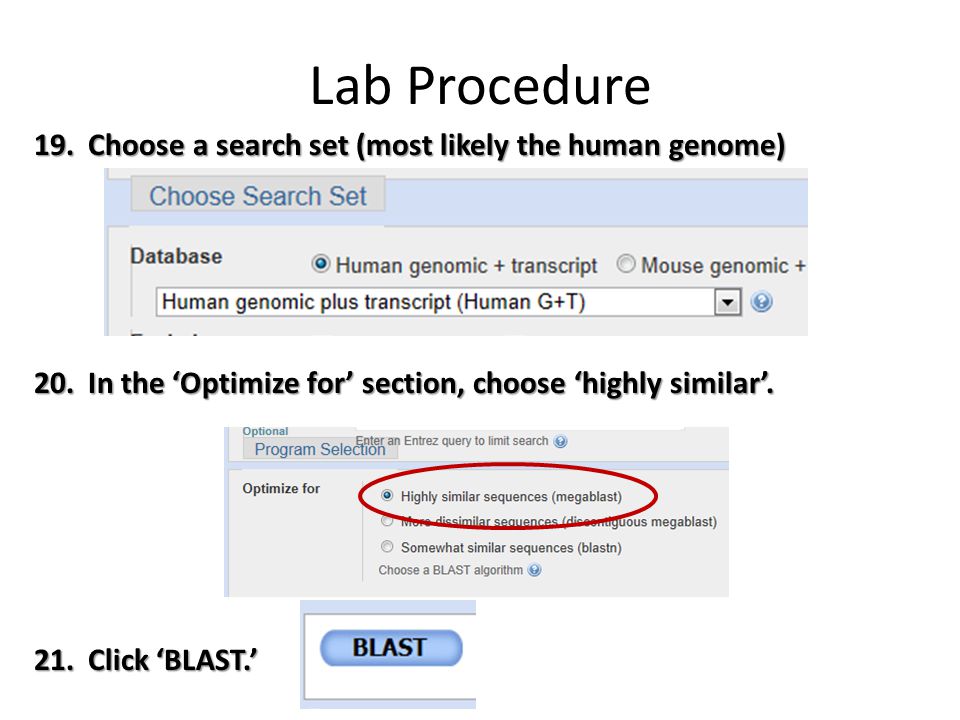
Blast results are reseted one hour after you have left your Blast result page. 12 Zeilen To see all available BLAST databases please run the command update_blastdbpl -. Under Choose Search Set select whether you want to search the human genome only mouse genome only or all genomes available.
Under Program Selection choose whether or not you want highly similar sequences or somewhat similar sequences. Choosing somewhat similar sequences will provide you with more results. Next we need to specify the database to blast against which in our case are the genome files Xeufasta Xpfasta Xgfasta and Xcfasta.
Makeblastdb command which is a part of BLAST package is used for creating BLAST databases from FASTA files. Makeblastdb -in Xeufasta -out Xeu -dbtype nucl. List of Significant BLAST Hits Figure 6b.
List of blastn hits that produce significant alignments with our query sequence Scrolling further down the output we find a summary table that shows all the sequences in the Refseq database that show significant sequence homology to our sequence Figure 6b. The BLAST Genomes search box located on the BLAST Basic Local Alignment Search Tool home page Figure 1 allows you to access the most complete genome assemblies for eukaryotic organisms. Use these steps to locate such assemblies.
Begin typing the name of the organism for example American to invoke the organism listing. DNA Data Bank of Japan National Institute of Genetics EMBL European Bioinformatics Institute GenBank National Center for Biotechnology Information DDBJ Japan GenBank USA and European Nucleotide Archive Europe are repositories for nucleotide sequence data from all organisms. Enter one or more queries in the top text box and one or more subject sequences in the lower text box.
Then use the BLAST button at the bottom of the page to align your sequences. To get the CDS annotation in the output use only the NCBI accession or gi number for either the query or subject. Database Name Source.
Species specific ESTs from NCBI dbEST downloaded 61417. Species specific assemblies of NCBI dbEST data performed by CGD. Species specific assemblies of filtered RNA-seq reads and unigenes performed by CGD.
Previous version of JGI assembly. Preformatted NCBI BLAST databases are available from this link httpsftpncbinlmnihgovblastdb. These databases include most of the databases that you can BLAST to using the NCBI BLAST function in Geneious such as nrnt EST refseq 16S Microbial and environmental samples.
To use the preformatted databases with your custom BLAST installation in. Then use the BLAST button at the bottom of the page to align your sequences. To get the CDS annotation in the output use only the NCBI accession or gi number for either the query or subject.
Reformat the results and check CDS feature to display that annotation. Click Select Columns or Manage Columns. What BLAST does When a search is run BLAST keeps a list of the database Subjects whose HSPs had the highest scores to your Query.
Typically 1000 are kept. The score of each HSP in the list is then converted into an E-value expect value. An E-value is the number of HSPs expected to have this score or higher purely by chance.
This tool compares nucleotide or protein sequences to genomic sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance of matches using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool BLAST algorithm. Genome Data Viewer GDV A genome browser for interactive navigation of eukaryotic RefSeq genome assemblies with comprehensive inspection of gene expression variation and other annotations. Other organism-specific databases for large-scale genome sequencing projects have been created for BLAST searches and include the human mouse rat zebrafish fugu Anopheles gambiae Arabidopsis thaliana and the Oryza sativa genomes httpwwwncbinlmnihgovBLAST.