
Laboratories and other facilities are categorized as BSL Biosafety Level 14 or as P1 through P4 for short Pathogen or Protection Level. These products are frequently referred to as microbial insecticides biorational or bio-insecticides.
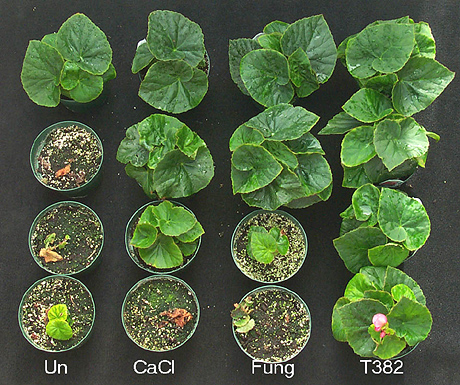
Beauveria bassiana is being evaluated as a biological control for seedling diseases.
Biological control of pathogens. Bacillus strains exhibit their biocontrol capacity predominantly through inhibitory activity on the growth of plant pathogens as well as inducing systemic resistance in plants and competing for ecological niches with plant pathogens. Our previous studies showed the presence of multiple biosynthetic operons for synthesis of non-ribosomal lipopeptides in the collection of natural isolates of. Biological control of pathogens and insect pests in agriculture and horticulture is based on the use of natural enemies of the agents that cause disease and infestations.
Plants are constantly under attack from all kinds of pathogens. The biological control of plant pathogens was detailed by Van Driesche Bellows 1996. It involves the ecological management of a community of organisms.
In the case of plant pathogens however there are two distinctions from biological control of organisms such as insects and plants. First the ecological management occurs at the microbial level typically in microcosms of the ecosystem such as leaf and. Some pathogens have been mass produced and are available in commercial formulations for use in standard spray equipment.
These products are frequently referred to as microbial insecticides biorational or bio-insecticides. Some of these microbial insecticides are still experimental others have been available for many years. Formulations of the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis or Bt for.
Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads Particular bacterial strains in certain natural environments prevent infectious diseases of plant roots. How these bacteria achieve this protection from pathogenic fungi has been analysed in detail in biocontrol strains of fluorescent pseudomonads. Alternative disease control is sometimes possible through development of crop plants resistant to disease.
Unfortunately however resistance is lacking or not available for many diseases caused by soilborne plant pathogens. Another biological means of controlling disease which is presently gaining much attention is biological control. Several systems of biological control are presently being.
Biological control was originally defined the action of parasites predators or pathogens in maintaining another organisms population density at a lower average than would occur in their absence. Biological control provided by these living organisms is especially important for reducing the numbers of pest insects mites and pathogens. It is an environmentally sound and effective means.
The soil the plant the pathogen and the biocontrol agent interact with each other through both biotic and abiotic signals many of which remain unknown. Beauveria bassiana is being evaluated as a biological control for seedling diseases. This will broaden the biological control spectrum of activity for this biopesticide since it also has activity as a pathogen of insect pests.
Mycoviruses of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 mycoparasitism of Sclerotinia minor and manganese-reducing microflora for Gaeumannomyces graminis var. Tritici are being examined for diseases caused by these pathogens. A biological hazard or biohazard.
The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC categorizes various diseases in levels of biohazard Level 1 being minimum risk and Level 4 being extreme risk. Laboratories and other facilities are categorized as BSL Biosafety Level 14 or as P1 through P4 for short Pathogen or Protection Level. Biological Control of Plant Pathogens The term biological control was first coined by Harry Smith of the University of California in relation to the biological control of insects.
He defined biological control as the suppression of insect populations by the actions of their native or introduced enemies. Since then many definitions have been suggested. Most of these are.
There are hundreds of biological control products available commercially for dozens of pest invertebrates vertebrates weeds and plant pathogens Anonymous 1995. The practice of augmentation differs from importation and conservation in that making permanent changes in a agroecosystem to improve biological control is not the primary goal. Biological Approaches for Control of Root Pathogens of Strawberry F.
Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Service 1636 East Alisal St Salinas CA 93905. Accepted for publication 23 July 2002. N and Bull C.
Biological approaches for control of root pathogens of strawberry. Biological control is a component of an integrated pest management strategy. It is defined as the reduction of pest populations by natural enemies and typically involves an active human role.
Keep in mind that all insect species are also suppressed by naturally occurring organisms and environmental factors with no human input.
