By generating a matrix bacteria in biofilms create a physically distinct habitat that provides shelter promotes the accumulation of nutrients and fundamentally alters both the physicochemical environment of the biofilm and interactions among the organisms therein. Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS.

6 Zeilen Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of.
Biofilms an emergent form of bacterial life. An emergent form of bacterial life. Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS. Importantly bacteria in biofilms exhibit a set of emergent properties that.
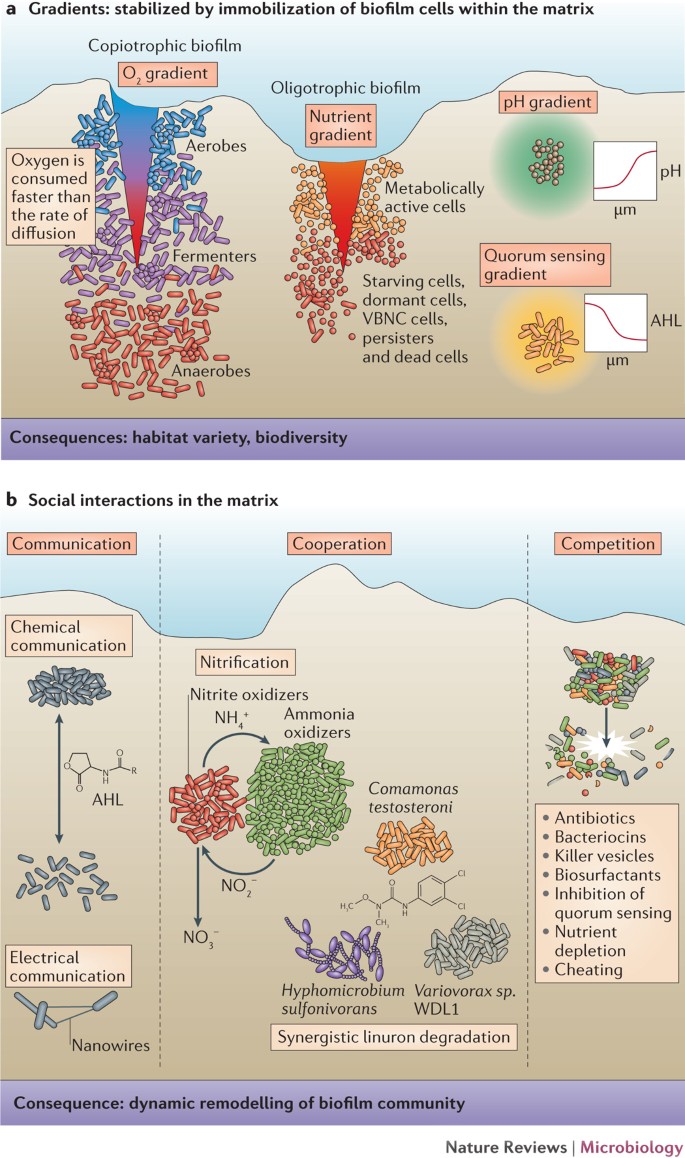
An emergent form of bacterial life The biofilm matrix. Most of the biomass of the biofilm comprises hydrated EPS rather than microbial cells 17. Heterogeneity and social interactions.
The organization of bacterial biofilms based on the matrix allows for a. Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS. Contend that the concept of the biofilm as an emergent form of microbial life relies on the supracellular organi zation that arises from the formation of the EPS matrix.
Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS. Importantly bacteria in biofilms exhibit a set of emergent. Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS.
An emergent form of bacterial life. Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS. Importantly bacteria in biofilms exhibit a set of emergent properties that.
Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS. Importantly bacteria in biofilms exhibit a set of emergent properties that differ substantially from free-living bacterial cells. In this Review we consider the fundamental role of the.
37 Zeilen Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self. By generating a matrix bacteria in biofilms create a physically distinct habitat that provides shelter promotes the accumulation of nutrients and fundamentally alters both the physicochemical environment of the biofilm and interactions among the organisms therein. In some instances emergent properties deriving from biogenic habitat formers in biofilms extend to the macroscale such as in structured biofilms that take the form.
6 Zeilen Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of. An emergent form of bacterial life Reference. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2016 14.
Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS. Importantly bacteria in biofilms exhibit a set of emergent properties that differ substantially from free-living bacterial cells. In this Review we.
Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS. Importantly bacteria in biofilms exhibit a set of emergent properties that differ substantially from free-living bacterial cells. In this Review we consider the fundamental role of the biofilm matrix in establishing the emergent properties of biofilms describing how the characteristic.
Figure 4 Tolerance of and resistance to antimicrobials. In the context of human health an important emergent property of biofilms is an increased ability to survive exposure to antimicrobial compounds including disinfectants toxic metals and small-molecule antibiotics which can occur by several mechanisms. Tolerance which is a non-heritable phenotype can arise when extracellular.
Bacteria An Emergent Form of Bacterial Life Nature Bacteria in natural conditions forms aggregates or communities ofsurface-adherent organisms embedded in an extracellular matrix called biofilmsIn biofilms the microorganismsare embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substancesEPS that are adherent to each other andor a surface. An emergent form of bacterial life. Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances EPS.
Importantly bacteria in biofilms exhibit a set of emergent properties that differ. Aug 11 2016 - Numerous metabolic functions social interactions and survival mechanisms are specific to or more pronounced in biofilms than in planktonic cells. In this Review Flemming and colleagues highlight the central role of the self-produced matrix in establishing these emergent properties of biofilms.
Bacterial biofilms are formed by communities that are embedded in a self.
