Contaminated water devastates health across the Aral Sea region Ill-conceived and badly managed farming methods have devastated the economy health and ecology of the Aral Sea Basin in Central Asia affecting millions of people. The remnants of it nestle in the climatically inhospitable heart of Central Asia to the east of the Caspian SeaThe Aral Sea and its demise are of great interest and increasing concern to scientists because of the remarkable shrinkage of its area and volume that began in the second half of the 20th centurywhen.

Results Infant mortality.
Aral sea health problems. The vanishing Aral Sea. Health consequences of an environmental disaster Pollution. No rivers flow out of the Aral Sea.
Water disappears through evaporation. Before construction of the. With the disappearance of rivers flowing into the Aral Sea area drinking water is.
There are basically no healthy children around the Aral Sea Zita Mazhitova general secretary of the Pediatricians Association of Kazakhstan. One of the largest global environmental disasters in the recent history which is being experienced by countries and the population of 62 million people in Central Asia is the tragedy of the Aral Sea that in its environmental climatic socio-economic and humanitarian consequences poses direct threat to the regions sustainable development health gene pool and future of the people residing. Compared with far eastern Kazakhstan the Aral Sea population seems more prone to develop cancer 34 35.
1980s the occurrence of liver cancer doubled 36 while the incidence of. Contaminated water devastates health across the Aral Sea region Ill-conceived and badly managed farming methods have devastated the economy health and ecology of the Aral Sea Basin in Central Asia affecting millions of people. It all started to go drastically wrong when planners decided to intensify cotton production in the 1950s.
The Aral Sea has shrunk to 10 of its former size Contaminated drinking water caused many problems and these were exacerbated when the water retreated. As the sea dried up toxic chemicals from the. As a result the areass inhabitants have suffered health problems at unusually high ratesfrom throat cancers to anemia and kidney diseasesand infant mortality in the region has been among the highest in the world.
Dust storm A plume of dust blowing southeastward from the dry seabed of the southern portion of the Aral Sea. The Aral Sea was once the worlds fourth-largest lake but an irrigation project drained nearly all the water. The consequences include the loss of a fishing industry salt-laden dust affecting crops and human health and an altered climate.
A dam has increased water levels in a small part of the lake called the North Aral. Results Infant mortality. Infant and under-five morality rates refer to the likelihood of a child dying before their first and.
Birthweight and post-natal growth. All of the Uzbek national health surveys mentioned above examined physical. Diarrheal disease represents a.
PUBLIC HEALTH PROBLEMS IN THE ARAL SEA REGION Covid strain that can fool three antibodies found in Mumbai Metropolitan Region This is one of three mutations K417N E484K and N501Y seen in the South African lineage said Dr Nikhil Patkar associate professor in haematopathology at Tata Memorial Centres Kharghar unit called ACTREC. The shallow Aral Sea was once the worlds fourth largest body of inland water. The remnants of it nestle in the climatically inhospitable heart of Central Asia to the east of the Caspian SeaThe Aral Sea and its demise are of great interest and increasing concern to scientists because of the remarkable shrinkage of its area and volume that began in the second half of the 20th centurywhen.
The dust salt and chemicals now coming off of the Aral Seas dried-up seabed are causing health problems for locals Credit. Taylor Weidman When whipped up. The ecosystem has collapsed the desiccated lake bed is laced with pesticides that are spread by dust storms and drinking water is polluted.
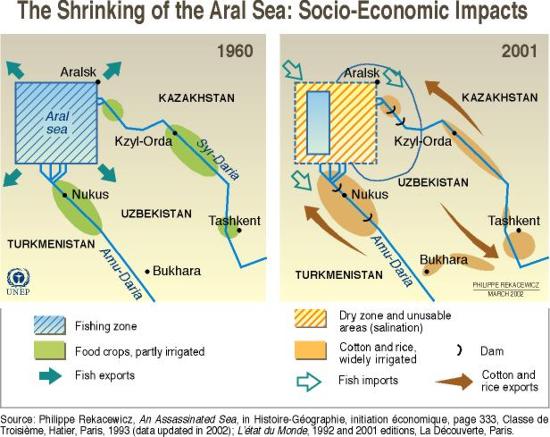
Aral Sea Activity Use the graphics to answer the following questions. What problem did the Soviet Union try to solve by building irrigation canals in the desert. They needed more farmland 2.
What percent of their total land was arable10 3. What does the word arable mean.