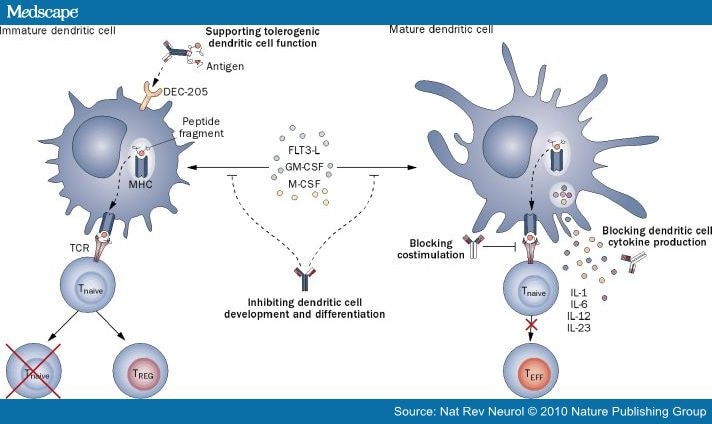
Provide insight into the underlying mechanisms by revealing that TIM-3 suppresses HMGB1-dependent endocytosis of extracellular DNA and the subsequent activation of the cGAS-STING pathway in intra-tumoral dendritic cells. Immature dendritic cells Dcs are characterised by high antigen uptake ability and poor T-cell stimulatory function.
About 60 of dendritic cells possessed the ability to take up antigen in both the in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Antigen uptake by dendritic cells. During an injury tissue dendritic cells such as LC in the epidermis capture the antigen and then under microenvironmental signals such as TNFα production in the dermis leave the nonlymphoid tissues through the afferent lymph veiled cells. Uptake of antigens from the intestine by dendritic cells. The intestinal immune system responds to ingested antigens in a variety of ways ranging from tolerance to full immunity.
How T cells are instructed to make these differential responses is still unclear. Dendritic cells DCs sample enteric antigens in the lamina propria and Peyers patches and tra. Uptake of antigens from the intestine by dendritic cells.
MacPherson G 1 Milling S Yrlid U Cousins L Turnbull E Huang FP. The intestinal immune system responds to ingested antigens in a variety of ways ranging from tolerance to full immunity. How T cells are instructed to.
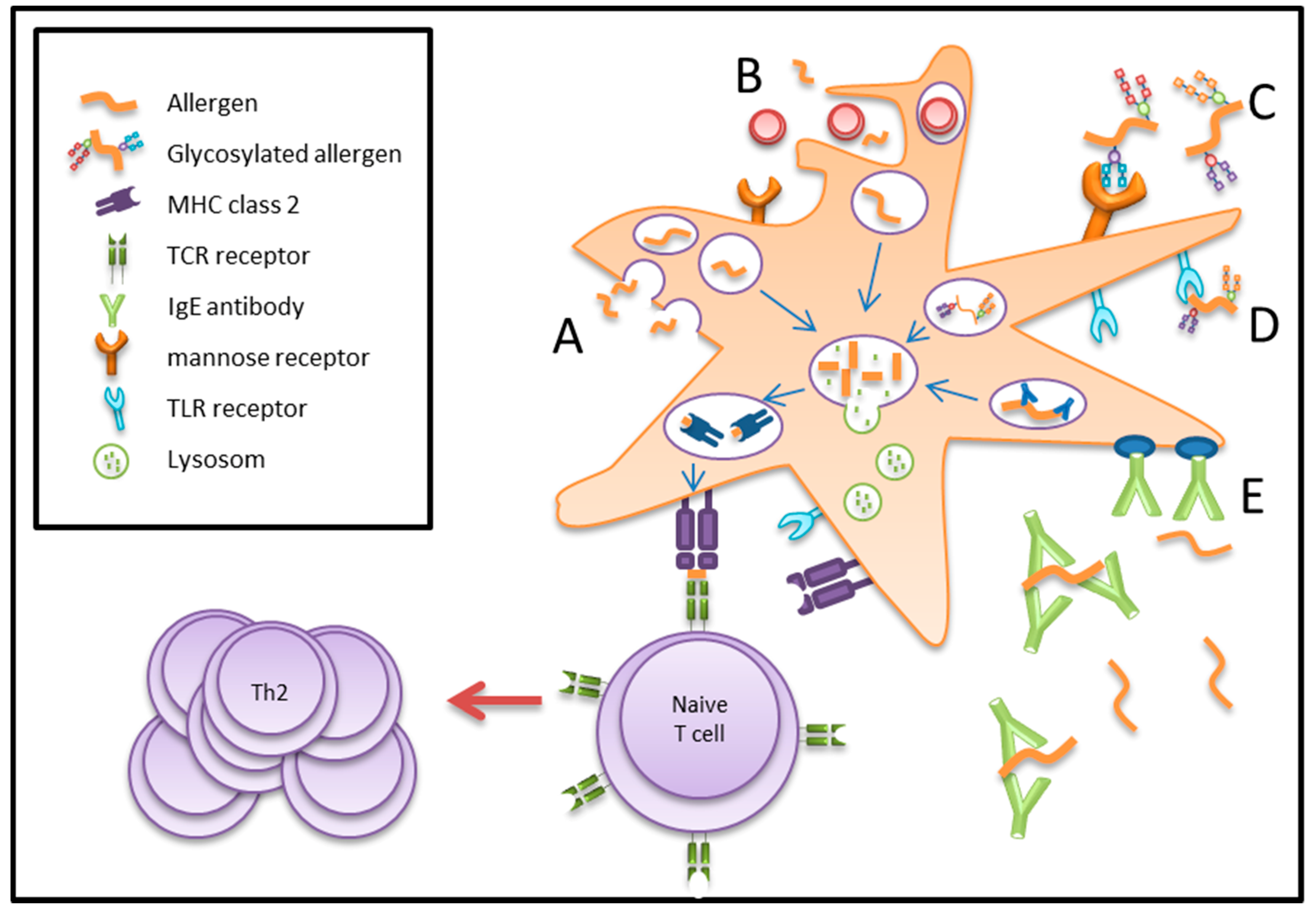
Dendritic cells are the most efficient antigen-presenting cells. They take up antigens and pathogens generate MHC-peptide complexes migrate from the sites of antigen acquisition to secondary lymphoid organs and finally they physically interact with and stimulate T lymphocytes. Indeed dendritic cells are the only antigen-presenting cells that induce the activation of resting T cells.
About 60 of dendritic cells possessed the ability to take up antigen in both the in vitro and in vivo experiments. The uptake of antigen occurred very rapidly reaching maximum values in terms of. In this chapter the major mechanisms of antigen uptake processing and presentation by antigen-presenting cells in particular dendritic cells are compendiously explored.
In the course of these processes immature dendritic cells mature into immunostimulatory cells able to activate CD4 and CD8 T cells. Initial uptake of exogenous antigens is provided by mainly three phagocytic pathways 1. As dendritic cells DCs are the most powerful APCs they are an attractive means to reinvigorate T cell responses.
An appealing strategy to use the effective Ag processing and presentation. CLEC12A-Mediated Antigen Uptake and Cross-Presentation by Human Dendritic Cell Subsets Efficiently Boost Tumor-Reactive T Cell Responses. Dendritic cells DCs which maintain tolerance and orchestrate T cell immune responses comprise a heterogeneous group of cells.
For example in the steady state murine spleen contains pre-DC-derived CD8 and CD8- conventional DCs. During inflammation monocytes become activated and acquire so. Immature dendritic cells Dcs are characterised by high antigen uptake ability and poor T-cell stimulatory function.
In contrast mature DCs have a high stimulatory function and poor antigen uptake ability. Inflammatory stimuli induce DC maturation and migration from nonlymphoid tissues to. Although immature dendritic cells have a considerable capacity to acquire antigenic peptides their ability to present these peptides is only initiated when the cells encounter an infection.
Bacterial products such as lipo-polysaccharide or inflammatory cytokines initiate a. Dendritic cells DCs are the primary antigen-presenting cells and play key roles in the orchestration of the innate and adaptive immune system. Targeting DCs by nanotechnology stands as a promising strategy for cancer immunotherapy.
Dendritic cells down-modulate their capacity to take up soluble antigens in response to exogenously added or endogenously produced ceramides. This is followed by an impairment in presenting soluble antigens to specific T cell clones while cell viability and the capacity to stimulate allogeneic responses or to present immunogenic peptides is fully preserved. Antigen uptake was examined by flow cytometry and confocal laser scanning microscopy in vitro using mouse bone marrow dendritic cells BMDCs.
The results showed that MAN-ALGALGOVA NPs facilitated antigen uptake of BMDCs and cytosolic release of the antigen. We conclude that antigen uptake can occur at the protrusive structures of dendritic cells that contain podosomal elements and this antigen can be subsequently processed by dendritic cells which might eventually result in T-cell activation. Blockade of the inhibitory receptor TIM-3 shows efficacy in cancer immunotherapy clinical trials.
De Mingo Pulido et al. Provide insight into the underlying mechanisms by revealing that TIM-3 suppresses HMGB1-dependent endocytosis of extracellular DNA and the subsequent activation of the cGAS-STING pathway in intra-tumoral dendritic cells. Dendritic cells DC are professional antigen-presenting cells characterized by their unique ability to stimulate naive T cells.
Because of their key role in linking innate immune activation with the induction of adaptive immune responses ex vivo and in vivo manipulation of DC is of special interest for the development of novel vaccination strategies. The most potent APCs are dendritic cells DCs which mature into professional APCs through the uptake of antigens. Immature DCs exhibit high antigen uptake ability while mature DCs are characterized by poor uptake of antigens and high expression of co-stimulator molecules such as MHCII CD80 and CD86 Banchereau and Steinman 1998.
This technology has been shown to improve antigen presenting cell uptake lymph node trafficking and B-cell activation through increased avidity and particle size. With a focus on design we.
