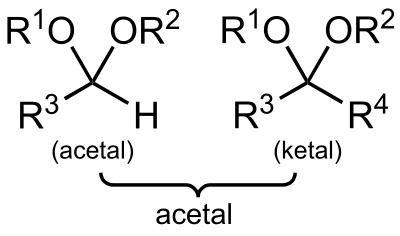
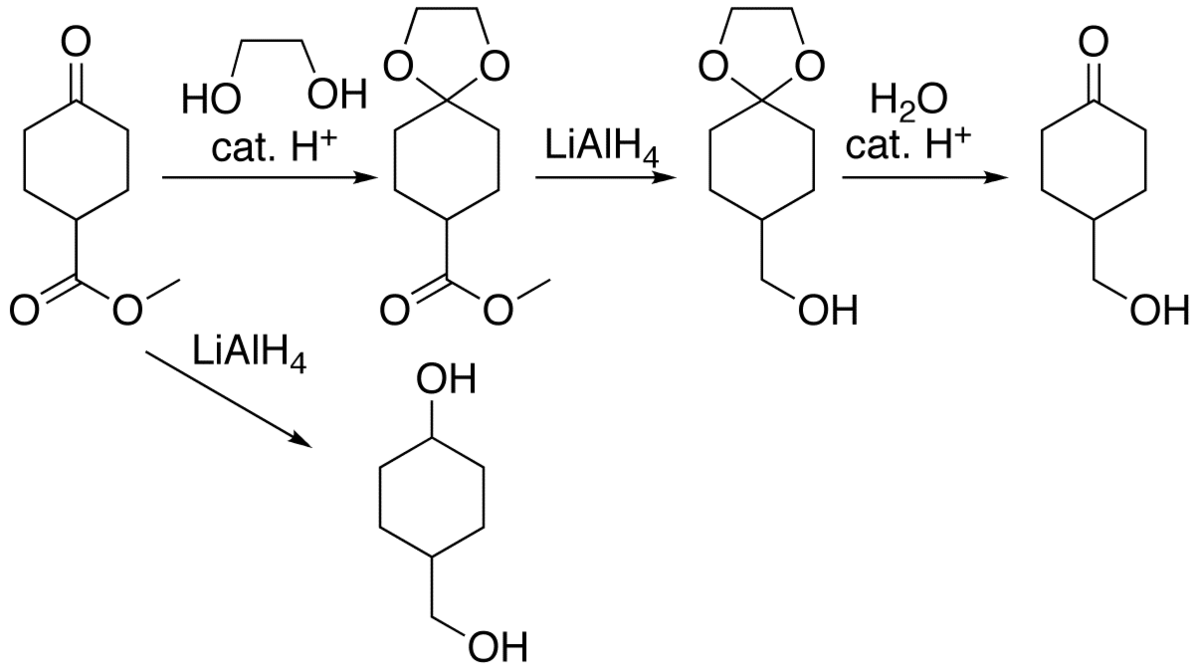
Acetals and Ketals. They can be used for example when a selective reduction of an ester is needed in the presence of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Acetal and ketal groups have been used as protecting groups for the 2-OH.
Acetals and ketals as protecting groups. Acetals and ketals are excellent protecting groups for aldehydes and ketones. In some reactions the electrophilicity of an aldehyde or ketone in a molecule. Acetals as Protecting Groups for Aldehydes and Ketones Acetals are the protecting groups for aldehydes and ketones.
They can be used for example when a selective reduction of an ester is needed in the presence of an aldehyde or a ketone. This problem is to disguise or protect group B in such a way that it cannot react. After group A is allowed to react the disguise of group B is removed.
The chemical disguise used with group B is called a protecting group or protective group. Acetals are among the most com-monly used protecting groups for aldehydes and ketones. Acetals as Protecting Groups.
The importance of acetals as carbonyl derivatives lies chiefly in their stability and lack of reactivity in neutral to strongly basic environments. As long as they are not treated by acids especially aqueous acid acetals exhibit. Acetals and Ketals.
Cyclic acetals and ketals are the most useful carbonyl aldehyde or ketone protecting groups. Common diols used to form ketals are show below in order of their relative rate of formation. 13-dioxanes cleave faster than 13-dioxolanes.
An undergraduate or graduate student in Chemistry may indeed carry out the above reaction in a round bottom flask using Methanol as the solvent in order to convert an aldehyde to an acetal as part of a Protecting Group strategy. Acetals are less susceptible to nucleophilic attack as compared to the corresponding Aldehyde and can therefore be carried along in a protected state during a multi-step. Because the acetal functional group is tolerant to very basic and harsh conditions forming acetals is a good way to protect an aldehyde or ketone.
For example suppose you wish to prepare the following alcohol from a β-ketoester. Acetal and ketal groups have been used as protecting groups for the 2-OH. These functions are removed under acidic conditions.
The ketal groups are deprotected more rapidly than the acetal type and 4-methoxytetrahydropyran-4-yl 18 which is removed in milder conditions than tetrahydropyranyl 17 has the advantage of no chirality. Ketals as protecting group Cyclic carbonates and cyclic boronates have also found considerable use as protective groupsIn contrast to most acetals and ketals the carbonates are cleaved with strong base and sterically unencumbered boronates are readily cleaved by water. Enol ethers of saturated 3-ketones are not usually obtained directly from the ketone and therefore are of little importance.
Part v Protecting groups Paul A. Clarke and William H. 11 Acetals and ketals Acetals are one of the most useful of the carbonyl protecting groups as they mask the.
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments.
A self-assembling supramolecular catalyst that hydrolysed dimethyl acetals and ketals such as 21 in water at pH 10. Pengfei Wang of the University of Alabama Birmingham has designed Org. A protecting group 23 for aldehydes and ketones that was efficiently removed by photolysis.
Acetals and ketals are readily deprotected under neutral conditions in the presence of acetone and indiumIII trifluoromethanesulfonate as catalyst at room temperature or mild microwave heating conditions to give the corresponding aldehydes and ketones in good to excellent yields. Acetals as protecting groups and thioacetals. This is the currently selected item.
Formation of imines and enamines. Formation of oximes and hydrazones. Addition of carbon nucleophiles to aldehydes and ketones.
Formation of alcohols using hydride reducing agents. Oxidation of aldehydes using Tollens reagent. In the present study protecting groups of moderate stability such as acetals and ketals were investigated as pendant blocking groups in polyvinyl phenols.
Polymers were obtained by reacting enol ethers with the phenolic side groups to form acetal or ketal blocked phenols. Acetals and Ketals as Protecting Groups So what we have is a reaction that we can use to. First protect a carbonyl group as a less reactive species.
Second do some reaction on another part of our moleculethat would have been incompatible with the carbonyl group. Third remove the protecting group to recover the carbonyl group.